The OECD.AI Policy Observatory is an inclusive platform that brings together resources and expertise from the OECD and its partners to facilitate dialogue and provide evidence-based policy analysis on the impact of AI. It is built upon the foundation of the OECD AI Principles, the first intergovernmental standard on AI adopted in 2019, endorsed by OECD countries and partner economies.
Emerj and the OECD have a collaborative relationship that spans multiple engagements. Emerj’s CEO and Head of Research, Daniel Faggella, initially gave a keynote address at the OECD’s symposium on life sciences AI in 2019. Subsequently, Daniel participated in the launch of the OECD’s AI Policy Observatory, where he conducted interviews with AI governance leaders for the ‘AI in Business’ podcast.
Earlier this year, Daniel represented Emerj at the OECD’s Fourth Global Forum on Digital Security for Prosperity, where he joined a panel discussion on security risks in AI. This ongoing partnership showcases Emerj’s involvement in policy discussions and knowledge sharing with the OECD on crucial topics related to AI, security, and collaboration between technical and policy-making communities.
The OECD Catalogue of AI Tools & Metrics addresses the challenges of explainability, transparency, and bias in AI systems by providing a platform for sharing and discovering tools and methods for trustworthy AI. The catalogue covers various technical, procedural, and educational tools.
The technical tools included in the catalogue address bias detection, transparency, and security, while procedural tools offer guidance on governance frameworks and risk management. The more education-focused tools focus on building awareness and upskilling stakeholders.
This article will examine and presents valuable insights from the top three tools featured in the OECD.AI Catalogue:
- IEEE Trusted Data and Artificial Intelligence Systems (AIS) Playbook for Financial Services: An industry-specific implementation guide to access curated, trustworthy data and AIS implementation requirements, leverage the sandbox/community to explore Ethically Aligned Design methodologies and certification programs for high-value AIS use cases.
- Generative Language Models and Automated Influence Operations- Emerging Threats and Potential Mitigations: This report examines the dynamic challenges of AI-powered influence operations, prompting proactive risk mitigation measures in a rapidly evolving landscape and emphasizing the need for informed decision-making and collaborative efforts.
- Mitigating Data Security and Privacy Risks in Generative AI: The article shows how to minimize the data security and privacy risks associated with the use of Generative AI. It also emphasizes the importance of a comprehensive strategy that includes data governance, ethical AI practices, and security and privacy controls.
IEEE Trusted Data and Artificial Intelligence Systems (AIS) Playbook for Financial Services
The Finance Playbook offers a practical implementation guide for technologists in the financial services industry. Incorporating IEEE’s Ethically Aligned Design, IEEE 7000™ standards, and ECPAIS certifications equips financial institutions with the necessary tools to prioritize human well-being and ethical considerations in the application of data and Artificial Intelligence Systems (AIS).
Furthermore, it addresses the global regulatory landscape and its impact on the future development of AIS and ethics, ensuring that organizations stay compliant and future-proof in their AI initiatives.
The business value of Version 1.0 of The Finance Playbook lies in its ability to harness cutting-edge thinking from financial experts in AIS (Artificial Intelligence Systems) and thought leaders at IEEE. By incorporating the globally recognized Ethically Aligned Design document and collaboration with leading policy organizations, this playbook provides a pragmatic and comprehensive guide for responsible AIS design consistent with compliance values worldwide.
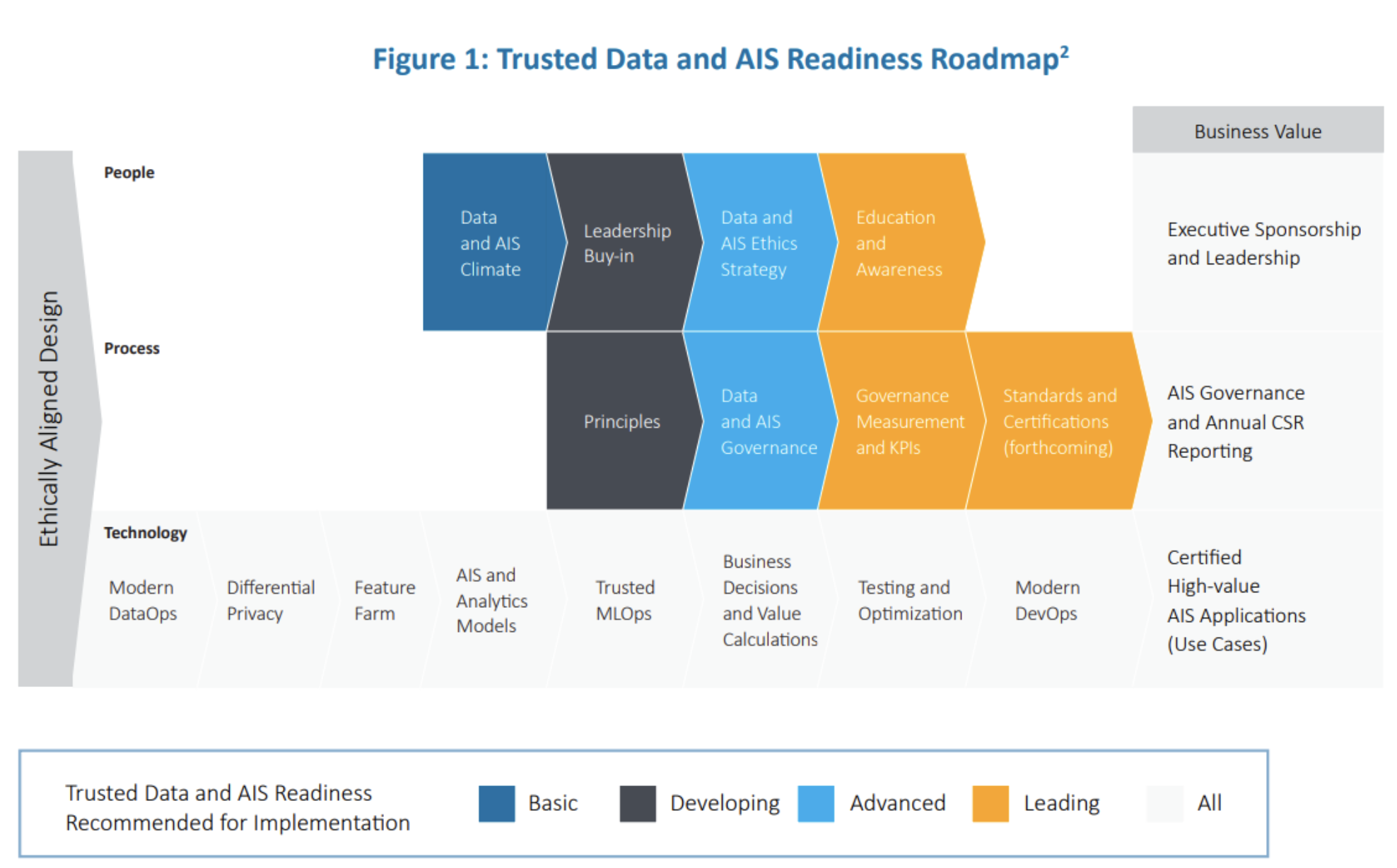
The playbook offers a platform for organizations to implement the Ethically Aligned Design ideology, enabling them to create value with data, advanced analytics, and AIS technologies. It focuses on three critical business blocks: technology, process, and people, providing insights and capabilities to develop trusted data and AIS practices.
The playbook aims to deliver business value through robust AIS governance and executive leadership by emphasizing high-value use cases, risk management and governance.
IEEE developed Trusted Data and AIS Readiness Roadmap to help guide organizations in the development of their trusted data and AIS in the near-term.
(Source: IEEE Finance Playbook Version 1.0 Trusted Data and Artificial Intelligence Systems (AIS) for Financial Services)
Business leaders can leverage the wealth of guidelines and principles outlined in various documents to inform their AI adoption strategies. With the contribution of ethical guidelines for AI released by private companies and industry leaders, multinational organizations can gain insights into best practices and responsible AI approaches and substantively reinforce their compliance efforts.
By studying the documents linked in the playbook, they can assess the evolving regulatory landscape and align their AI initiatives with ethical considerations that will likely be the foundation of future AI legislation worldwide.
Generative Language Models and Automated Influence Operations- Emerging Threats and Potential Mitigations
The research paper explains that, although numerous strategies are proposed to manage the threat of AI-generated influence operations, none are required to meet all the criteria to be effective. The four criteria mentioned are:
- Technical feasibility
- Institutional feasibility
- Robustness against second-order risks
- High impact
Each mitigation strategy currently fulfills only some of these requirements. Additionally, the widespread availability of large language models through paid APIs and forthcoming releases makes it nearly impossible to prevent their use in generating disinformation.
However, it also emphasizes that the existence of challenges does not justify defeatism. AI developers are responsible for taking reasonable steps to minimize the harms caused by their models, social media companies must actively combat misinformation, and policymakers should consider their role in addressing the issue.
It’s important to acknowledge that while mitigation strategies targeting AI-generated content may not completely solve the problem, efforts should still be made to address the inherent challenges associated with AI-generated influence operations.
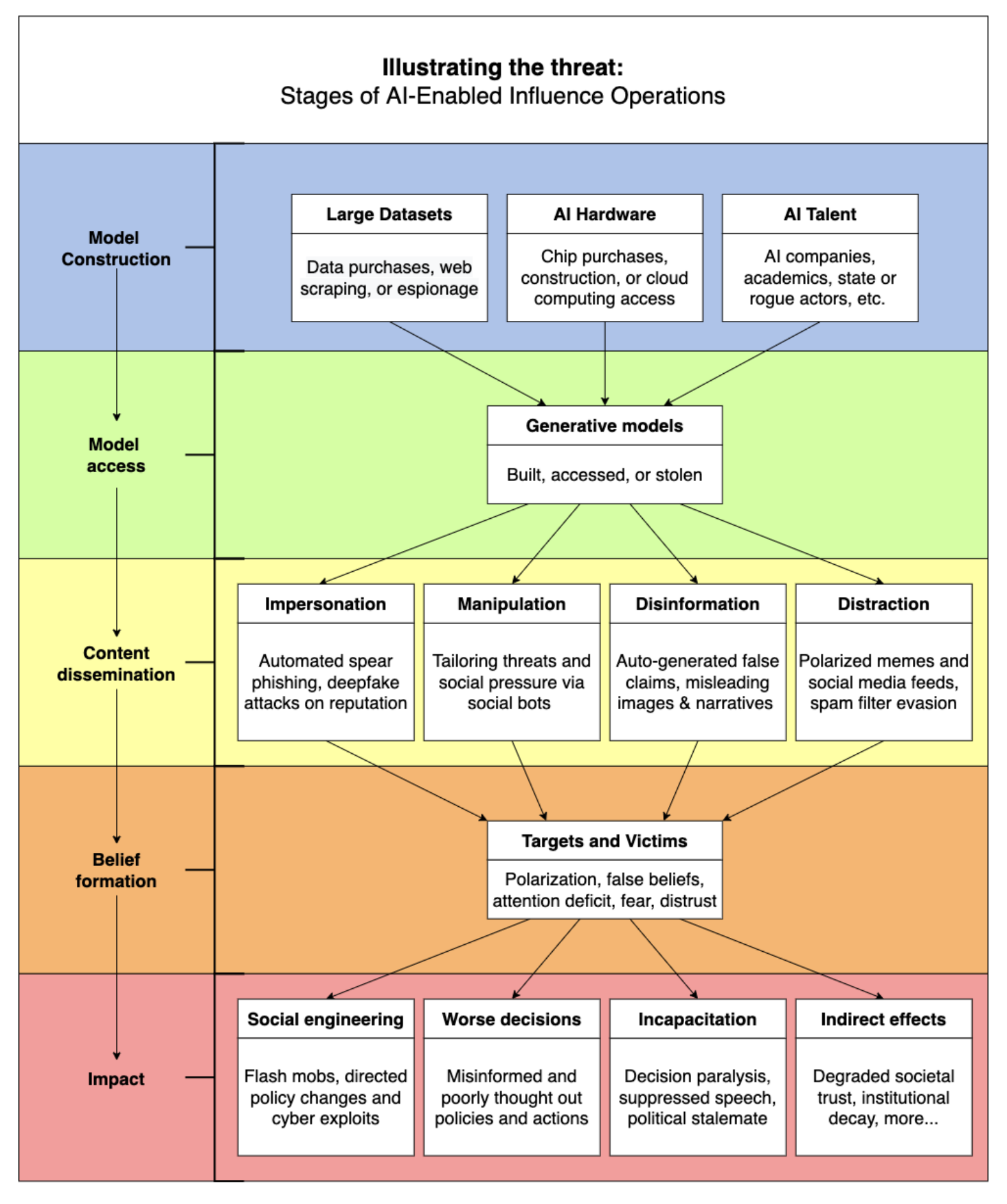 Stages of intervention of AI-enabled influence operations. To disrupt a propagandist’s use of language models for influence operations, mitigations can target four stages: (1) Model Design and Construction, (2) Model Access, (3) Content Dissemination, and (4) Belief Formation.
Stages of intervention of AI-enabled influence operations. To disrupt a propagandist’s use of language models for influence operations, mitigations can target four stages: (1) Model Design and Construction, (2) Model Access, (3) Content Dissemination, and (4) Belief Formation.
(Source: Generative Language Models and Automated Influence Operations- Emerging Threats and Potential Mitigations)
The paper delves into influence operations, explaining what they are and why they are carried out. By understanding the motivations behind these operations, businesses can gain a deeper awareness of the potential risks they may face. A section also explores the impact of influence operations, emphasizing their significance in today’s digital landscape.
Much of the paper focuses on generative models, particularly language models, and their role in producing disinformation. It explains how these models are built and highlights the accessibility and diffusion of generative models, which contributes to the proliferation of AI-generated content. Businesses can better comprehend the risks associated with such technologies by analyzing the connection between generative models and influence operations.
Business leaders can leverage the insights in this paper to facilitate the adoption of AI in their organizations. Firstly, they can comprehensively understand the threat landscape surrounding AI-generated influence operations. By analyzing the paper’s contents, they can assess the risks associated with AI adoption and develop tailored mitigation strategies. This knowledge enables leaders to make informed decisions about implementing and using AI technologies within their organizations.
Furthermore, executives can strengthen their organizational policies and guidelines related to AI adoption. By updating or creating new policies, leaders can address the challenges posed by AI-generated influence operations. These policies may cover data handling, model usage, content verification, and employee training. Implementing robust policies fosters a culture of responsible AI usage within the organization.
Mitigating Data Security and Privacy Risks in Generative AI
The article addresses the significant emergence of generative AI and its implications for data security and privacy.
It begins by highlighting the surge in investment in generative AI start-ups, underlining the growing significance of this technology in the industry. Further, it focuses on mitigating potential data security and privacy risks while harnessing the power of generative AI.
It poses critical questions regarding sharing sensitive information with Large Language Models (LLMs) and the potential risks of unintended data exposure. To address these concerns, the article presents a comprehensive checklist for business leaders to follow when engaging with generative AI tools.
The checklist covers opt-in/opt-out mechanisms, data retention, data usage for training and improvement, content filtering, and compliance traceability. By addressing these key considerations, the article aims to assist business leaders in making informed decisions regarding adopting generative AI while safeguarding data security and privacy.
It also underscores the need for organizations to balance leveraging the benefits of generative AI and ensuring robust measures are in place to protect sensitive information. Overall, the article guides business executives in navigating the evolving landscape of generative AI and its associated data security and privacy risks.
By understanding the potential challenges and following the provided checklist, organizations can ensure the protection of sensitive information while harnessing the benefits of generative AI.
Such information empowers businesses to adopt generative AI technologies confidently, enhance operational efficiency, drive innovation, and maintain customer trust. The content can be accessed on the website, published, or shared through relevant industry platforms, blogs, or newsletters catering to business leaders and professionals interested in AI, data security, and privacy.
Per the report, business leaders can drive AI adoption in their companies by:
- Exploring generative AI solutions like Jasper.ai, Midjourney, and Azure OpenAI services to identify relevant applications for their business.
- Understanding how data is processed and taking necessary steps to mitigate security and privacy risks.
- Reviewing the checklist provided in the passage to ensure adherence to corporate policies and mitigate data privacy and security risks.
- Partnering with model providers that support training new proprietary models (if necessary) while ensuring compliance with data privacy and security measures.
By following these steps, companies and businesses can gain insights into the potential of generative AI, address data security concerns and strategically incorporate AI technologies into their business operations.