
Today, two highly discussed disruptive technologies are artificial intelligence and blockchain. In this piece, we aim to highlight projects where AI and blockchain might be used together to support the B2B environment.
Blockchain is a technology that can help track transactions between users in a public ledger which was developed originally for Bitcoin. It is now used commercially for various applications such as tracking ownership documents, digital assets or voting rights.
Both AI and blockchain involve technical complexity and there seems to be a sense of agreement among experts that these technologies will have serious business implications in the next five to ten years. The joint use of the two technologies might alter the tech and business paradigm significantly enough for business leaders to take more notice of developments in this space.
We list out a few of the most prominent projects for which AI and blockchain technologies form the core of the product or service. We do this by highlighting select use cases and companies which are actively moving towards commercialization.
In the context of how AI and blockchain may be used together, it might be useful for business leaders to understand how AI can help Blockchain and vice versa. Some of the applications would be:
- AI Marketplaces
- Crowdsourced Predictive Models for Hedge Funds
- Investment Management Platforms
Avoiding Hype: Considerations for a Business Reader
While this article aims to serve as a look ahead at the direction of blockchain and AI, we believe the area is still in its nascency and is not yet providing major opportunities for businesses.
Because artificial intelligence and blockchain are “buzzwords” today, we encourage business readers to avoid hype by taking strong consideration of company factors — such as AI leadership and a technology’s real-world use cases — when researching AI and blockchain possibilities for their company.
Emerj CEO Dan Faggella warns, “There’s a lot of hype and a lot of purported excitement around these terms. Believe us, because we see it every day.”
“Anyone can slap the word artificial intelligence or blockchain in front of an existing technology conference, charge $500 more and sell 50-percent more tickets,” he adds.
While we do not discourage the idea that AI and blockchain could combine to do something useful, we have not found any tangible real-world examples of the combination being a critical part of any business solution.
The concepts of companies listed provide a unique look at what AI and blockchain could do for businesses in the future, but we believe all applications found are still too nascent to create an impact.
We at Emerj have covered and researched a tremendous number of applications across various industries, from banking to drug development to retail and more. Through this research, we see that the combination of AI and blockchain is unlike other well-understood AI strategies such as machine learning.
While many business leaders now understand how machine learning can be implemented into their company, the same is not true for blockchain. When AI is combined with blockchain, possible modern-day solutions may seem even fuzzier.
When researching young companies, such as those listed, with no marquis clients or proof of product value, we find team leadership background to be crucial in determining if the company credibility.
Along with researching leadership backgrounds for the listed applications, we’ve also looked into their investments. When factors such as leadership and case studies are not present, we find strong investment history to be a sign that the company offers a strong value proposition or can articulate a relevant problem that it is solving.
While Emerj researches a company through primarily public materials, a venture firm will often put a company through months of in-depth vetting before choosing to invest. Details investors often analyze include the company’s future plan, revenue model, leadership experience and team dynamics.
“Investment money from very reputable investment firms, such as DFJ, Andreessen Horowitz, Sequoia, essentially is a signal that under intense scrutiny, the business idea of a company holds up. When we are unable to see marquis clients and see case studies, we like to see that positive signal.” (Dan Faggella, CEO, Emerj)
It is worth noting that many of the listed companies below have raised money from initial coin offerings. Coin offerings come from cash of individual investors, rather than venture firms. This does not provide the same trust signal that it would if a major venture firm were to invest the same amount of funds.
“Although an initial coin offering doesn’t bode poorly, it doesn’t help to bode well,” says Faggella.
The applications in this report should not be seen as immediately transformative, but they should be seen as representative ideas of how blockchain might combine with AI to garner business value in the future. While these companies do not have the background we regularly search for, we believe they are still ahead of the curve in terms of experimenting with this combination.
To learn more about how to find credible AI use-cases, check out our guide: Separating Artificial Intelligence Hype from Reality – Three Simple “Rules of Thumb”
AI Marketplaces
SingularityNET
SingularityNET, an Amsterdam-based non-profit organization founded in 2017, claims to be a decentralized marketplace for AI algorithms. The company was founded by CEO Ben Goertzel, a chair of both the OpenCog Foundation and the Artificial General Intelligence Society.
SingularityNET offers a platform where developers or AI vendors can offer their hardware or software services in exchange for other AI services or cryptocurrency. SingularityNET’s currency is called “AGI tokens.” The organization claims that exchanges between parties in the marketplace are facilitated by means of blockchain-based smart contracts.
According to Investopedia, smart contracts are self-executing contracts where the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller is directly written into lines of code
The organization also claims that the marketplace is open-source where businesses and software developers receive payment in the form of cryptocurrency tokens in return for adding an AI or machine learning service to the marketplace ecosystem.
According to a whitepaper from SingularityNET they claim their marketplace functions by providing buyers and sellers with a set of standard AI software and hardware service APIs that can be integrated into smart contract templates. The templates are also provided by SingularityNET.
For example, this might enable companies organizations and individual developers to buy and sell large-scale AI services such as:
- Image and video processing services: Such as those that identifying people in videos, or generate text descriptions for a particular image.
- Language processing services: Text summarization and abstraction, language translation or text-based sentiment analysis
- Access to curated datasets to train AIs: Marketplace customers might share data such as background knowledge (i.e. social media data) to help train AIs that can then be used for analysis of other datasets.
- Companies could also simply request to have a particular dataset analyzed from other participants in the marketplace.
Below is a video where Ben Goertzel explains (from 3:23 minutes in) how SinglularityNET works at the World Blockchain Forum held in London:
To access the marketplace customers need to login through GitHub’s web portal where they can then access the SingularityNET app, a discovery tool for AI services on the marketplace. We could not find any demo for how customers might use the SingularityNET app on GitHub.
Through the GitHub app, users can search for the kind of AI service they require and will be automatically matched with the AI service that fits the search requirements, called an “agent.” Companies or businesses can then buy the agent service, or sell their own services using SingularityNET AGI tokens and smart contracts.
Although the project is still highly nascent with not much to show yet in terms of measurable robust results, SingularityNET claims that their crowdfunded ICO raised over $36 million within the first minute of its launch.
Aside from the company’s CEO, SigularityNET claims that their in-house technology team is also complemented by dedicated partnering teams from Hanson Robotics (Makers of Sophia Robot), Mozi Health (focussed on biomedical AI) and iCog Labs.
DeepBrain Chain
DeepBrain Chain is a non-profit organization founded in Singapore with around 35 employees. The organization claims to be using AI and blockchain technologies to develop a distributed AI computing platform.
According to a whitepaper from DeepBrain Chain, the company aims to provide a marketplace for AI hardware computing resources through a network where all participants of the system form parts of different training ‘nodes’ depending on the level of computing power available.
These nodes in the DeepBrain Chain network might be large nodes such as mining pools which are most commonly engaged in mining the DeepBrain Chain token. Medium-sized nodes use cloud computing services like Microsoft Azure or possibly home computers to train algorithms. These large or medium nodes can be rented out to companies or businesses that need the computing resources for AI projects and applications.
Home computer machinery, cloud services and individual users would be part of a medium sized node. Larger heavy computing resources used for mining the DBC coin would automatically form the larger computing nodes in the network.
The 5-minute demo below from DeepBrain Chain explains how node networks might be used by individuals or businesses to train an AI algorithm:
The entire network comprises of miners, or individuals who join the system by installing the DBC software which automatically allows them to be part of a particular node based on their computing power.
To pay for AI training services, the miner can toggle to a training screen and fill out their training requests, according to the demo video. As the AI is being trained, the log of code will be monitored and recorded for the user to look through in real-time or after the training. The program also notifies a user on its training dashboard if any anomalies or issues occur during training.
After training is complete, the miner is prompted to give feedback about the technology which trained the user’s AI. They then will pay the trainer in tokens for the service.
Miners can also upload and rent out their own datasets on the platform.
For example, AI vendors might upload data and models needed for neural network computation to the DBC decentralized storage network and then submit computing requests to use the network’s capabilities.
Below is an image from DBC showing the organization’s business model framework:
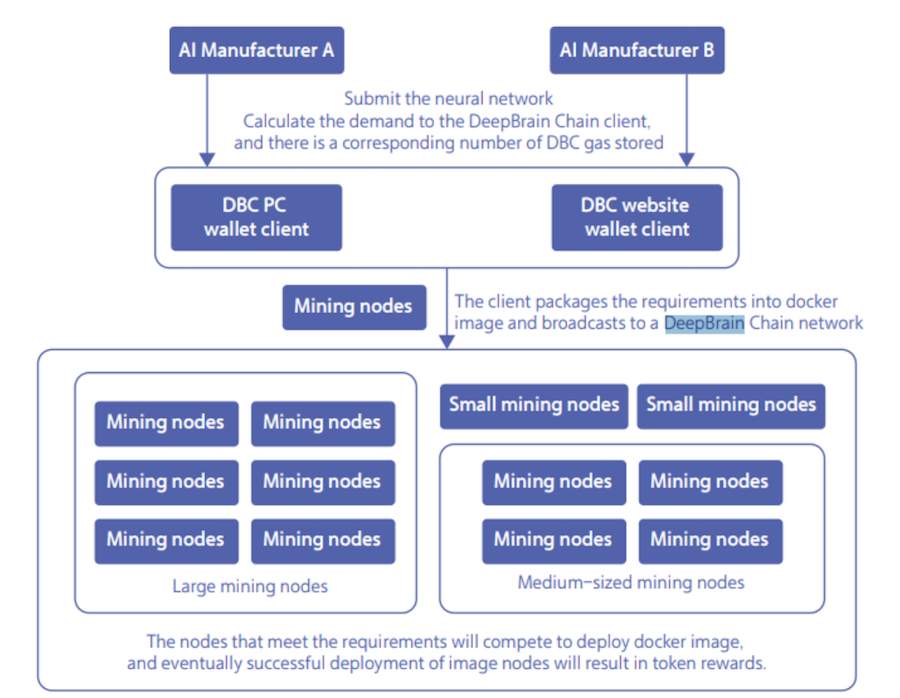
In addition, DBC claims that their platform can also be used by companies and developers to share datasets and as a trading platform to share artificial neural networks. We must add here that there was no evidence of the organization having shown measurable results.
Deepbrain Chain’s head of AI, Dongyan Wang previously earned a Ph.D. in Electronics and Computer Science from the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee. He has also held positions at Samsung, CIisci, and NetAPP. More recently he was the Global AI Leader of Midea Group, a Chinese Fortune Global 500 Company.
DeepBrain Chain has also signed a partnership with SingularityNET to allow AI agents on the SinularityNET marketplace to use the computing resources offered by the DBC marketplace. The company also seems to be offering computing ‘clusters’ for miners around the world to buy and claim that they have received around $100 million in pledges so far although we could not independently verify this claim.
Crowdsourced Predictive Models for Hedge Funds
Numerai
Numerai was founded in 2015 in San Francisco and is part of a hedge fund that was designed to gain prediction models and trading strategies from companies and developers who join the platform.
Numerai holds a weekly data science competition where predictions of their hedge fund performance for the coming week can be submitted by any user. A weekly prize is paid out to the top performing users in the form of Numeraire (NMR), an Ethereum ERC20 token created by Numerai in June 2017.
- Each week users can download two sets of data from Numerai’s site. Training data can be used to train the user’s machine learning models, which will attempt to predict the results. Users will submit predictions using the second tournament dataset, according to the company.
- Once users submit their predictions of the hedge fund’s future performance, they are scored based on the consistency and accuracy of their model’s performance.
- The best performing models can win the weekly prices denominated in NMR and also in Ethereum’s cryptocurrency Ether (ETH).
Numerai claims that they synthesize features from the top performing models each week to create a collective AI model that controls the investment strategy for the capital in the Numerai hedge fund. We must state here that we could find no further details of the hedge fund or its performance so far.
Below is a video from Numerai where industry experts and the company leadership explain the new model of the hedge fund:
We could find no further demos or interface images for the Numerai platform at the time of writing.
According to the USD exchange rate provided by CoinMarketCap, one NMR seems to be worth around $7.56 today.
Numerai CEO Richard Craib earned a BA in Mathematics from Cornell. We were unable to find any C-level executives with AI experience on the company’s team.
From our research, we also could find no evidence of Numerai having collaborated with marquee companies in AI or blockchain projects.
Investment Management Platforms
Peculium
Luxembourg-based Peculium was founded in 2017 and has around 45 employees.
Peculium is a savings and investment platform that claims to help investors automatically manage cryptocurrency portfolios. The company claims that their asset management solution can be used in different degrees of autonomy. This includes a completely autonomous version suitable for individual investors and a customizable version suitable for professional traders, larger corporations and stock brokers.
The company claims it has developed an AI advisor called AIEVE, which uses automated machine learning to learn from the analysis of historical information about cryptocurrency markets.
Peculium says data analyzed comes from online content including real-time financial markets covering cryptocurrency, news media, online research or published books. The company claims its AIEVE can read and analyze data in eight different languages.
According to a whitepaper from Peculium, larger businesses and corporations can invest through the Altreus, the company’s investment platform where a smart contract can be viewed through the platform. The smart contract specifies a predefined contract period after which it automatically initiates returns for a predefined portion of gains to the financial firm. [[0]]We could find no robust demo videos explaining how the Peculium platform operates.
There wasn’t much by way of results that we could find for how Peculium asset and investment management solutions performed although a post in the Medium claims that from January 14th to April 14, 2018, AIEVE was able to increase the value of savings from investments managed by her by 88 percent.
Abed Ajraou Peculium’s Chief Data Officer earned a Master’s Degree in Computer Science from Polytech Nice Sophia in France and previously taught in the Kedge Business School and the University of Paris-Sud. [[]] Airaou has also served as the Head of Business Intelligence at SoLocal Group and was an Information Management Manager at Accenture.
The Future of AI and Blockchain – What Can Businesses Expect?
From our research, we identified the following factors as key for business leaders to understand how AI and blockchain might disrupt businesses in the future:
- Due to the enormous disruptive potential in the combination of AI and blockchain technologies, business leaders might need to understand the new ways in which AI services could be used in the future.
- As with projects like SingularityNET and DeepBrain Chain, AI services and cloud-computing resources seem to be moving towards a marketplace ecosystem. Business leaders can probably expect more granularity in AI services. These services could move from identifying objects in an image to specifically identifying moving objects in real-time.
- Many of the projects are highly nascent and on the road to commercialization:
- The technical complexity involved in AI or blockchain individually by themselves is significant enough for businesses to undertake projects in. Applying these technologies jointly for solving B2B business issues at scale still seems to be at least five years away at this point.
- AI vendors and manufacturers might also find future opportunities using blockchain technologies.
- It might be common in the future to see cases where AI might help blockchain projects such as improving scalability or security. There also seem to be several opportunities for blockchain to improve existing AI projects like in helping humans and AI understand why a particular decision was made by the AI engine or in lowering the capital costs for AI services through marketplaces.
Header image credit: Medium







