Founded in 1982, Cigna is a healthcare and insurance company based in Bloomfield, Connecticut. Cigna is a Fortune 15 global company and employs over 70,000 individuals. Cigna offers health, life, and accident insurance. They also offer Medicare and Medicaid products.
In 2022, Cigna reported revenue of $180.5 billion. For 2022, Cigna’s adjusted income from operations was $7.3 billion, up from $7.0 billion the previous year. Cigna has over 175 million customers.
Cigna has implemented AI through partnerships with several providers of AI tools. This article will examine four use cases demonstrating how Cigna uses AI to benefit both patients and employees.
- Determining a customer’s payment eligibility: Using a rules-based system to process and assess claim payout.
- Improving patient outcomes: Using predictive analytics to help patients overcome chronic conditions.
- Recommending roles to employees: Combining data, automation, and deep learning to guide employment opportunities aligned with an employee’s strengths and skills.
- Making preliminary diagnoses: Using an inference engine and a classification algorithm to provide initial diagnosis and appropriately triage patients.
Determining a Customer’s Eligibility for Payments
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) introduced new requirements for electronic submission of healthcare information. Maintaining HIPPA compliance is essential, as breaches can be costly.
For the healthcare industry, a data breach per record costs $429 and is potentially accompanied by investigation, fines, and monitoring for several years following an incident. Cigna wanted a better way to process resulting claims and determine customer eligibility.
They partnered with Progress Corticon to accomplish this. The solution relies on a business rules management system (BRMS). This solution:
- Automated critical business decision-making
- Enables an agile approach to create, test, and deploy new business rules or change existing regulations.
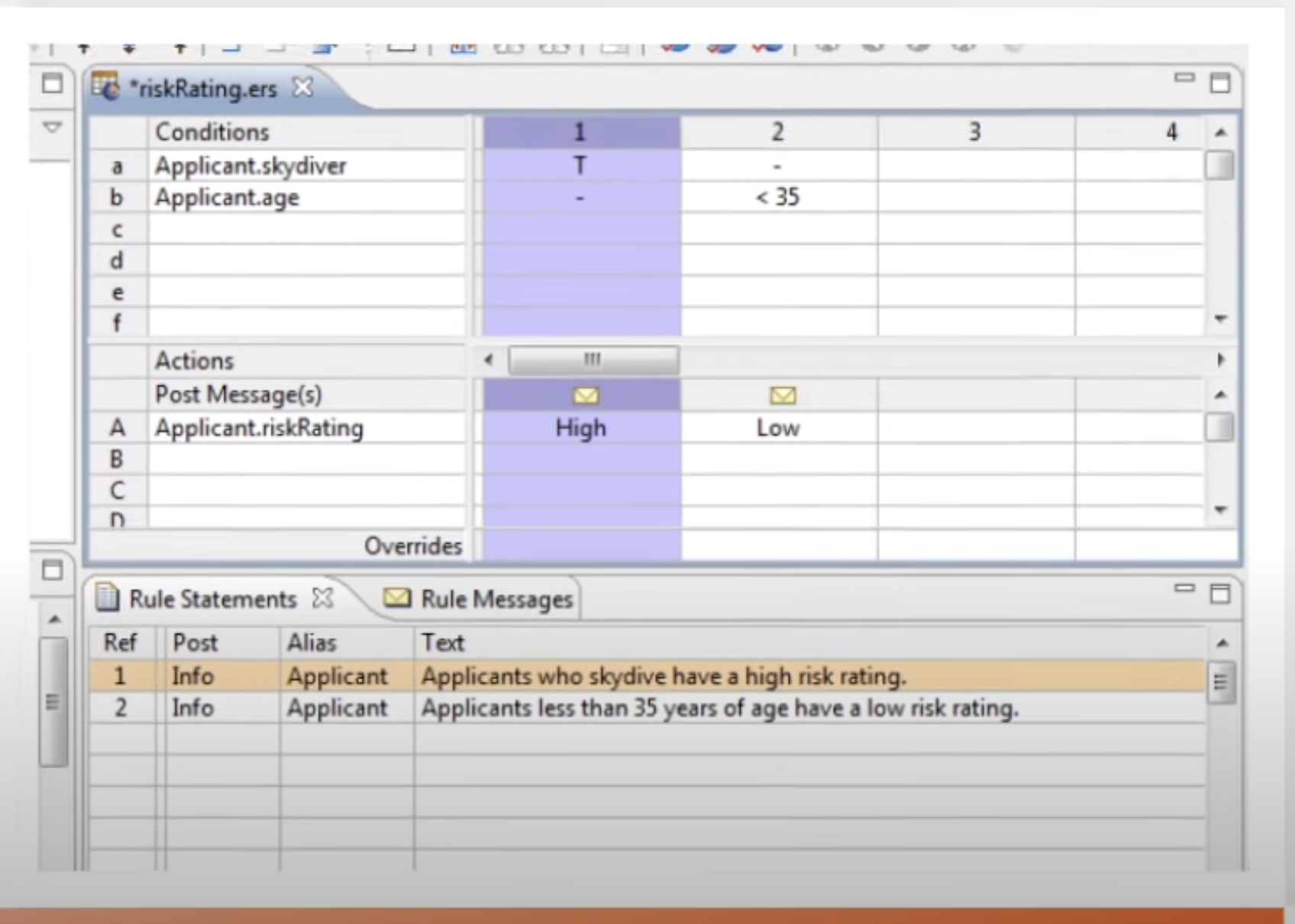
Screenshot of Progress Corticon’s Intuitive Decision Modeling Interface (Source: Progress)
Corticon determines a customer’s eligibility for payment based on multiple factors, including but not limited to the following:
- Coverage
- Medical procedure
- Party who submitted the claim
Corticon has allowed Cigna to centralize its rules-based processing. As a result, the claims routing process has improved in the following ways:
- Efficiency of the claims routing process
- Increased accuracy of the claims
- Reduced maintenance
The benefits of automating parts of the claims processing pipeline are not without drawbacks and possible detrimental financial consequences. Cigna has been subject to a federal lawsuit. The class-action lawsuit filed in California in late July alleges that Cigna used a procedure-to-diagnosis (PXDX) computer algorithm to reject 300,000+ claims during two months last year.
The lawsuit alleges that Cigna doctors reject claims instantly without ever opening the patient files. The lawsuit, filed on behalf of two California Cigna members, seeks unspecified damages and a jury trial.
Improving Patient Outcomes
According to Gina Papush, Global Chief Data and Analytics Officer at Evernorth, a large portion of healthcare costs in the United States consists of treatment related to chronic conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Evernorth, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Cigna Corporation, uses machine learning to predict chronic conditions like these before they occur.
In an online event hosted by VentureBeat, Papush mentions, “We really believe that healthcare in many ways will be enabled and transformed through the use of actionable intelligence.”
Papush explained how health services providers often find out about a diagnosis after the course of treatment has been decided. This limits their ability to provide these customers with the specialized support they need and help them connect with their treating physicians.
Their approach has been to leverage data from traditional and alternative sources to determine a prediction of likely diagnosis before diagnosis. She explained how they follow up with outreach to alleviate the burden on the patient by helping them figure out coverage and how to navigate treatment options.
The machine-learning-driven outreach has led to more patients taking advantage of the advice. Through a case study on breast cancer, Cigna saw 60% more patients take advantage of recommended clinical programs and specialized advice.
They also provided outreach to patients likely to experience adverse events from COVID-19. This has led to better patient outcomes and lower-cost treatment.
Recommending Roles to Employees
Cigna relied on AI when making significant changes to their internal talent management system in response to a substantial issue they faced: their employees had an easier time finding open Cigna positions on LinkedIn than they did through Cigna’s internal system.
Cigna wanted to utilize its existing talent pool to fill openings and minimize losing talented employees to external competition. It’s costly for companies to replace employees. According to the Society for Human Resource Management, finding and training an employee’s replacement costs 6-9 months of that employee’s salary.
Cigna chose the AI-powered HR platform Phenom to assist with the overhaul.
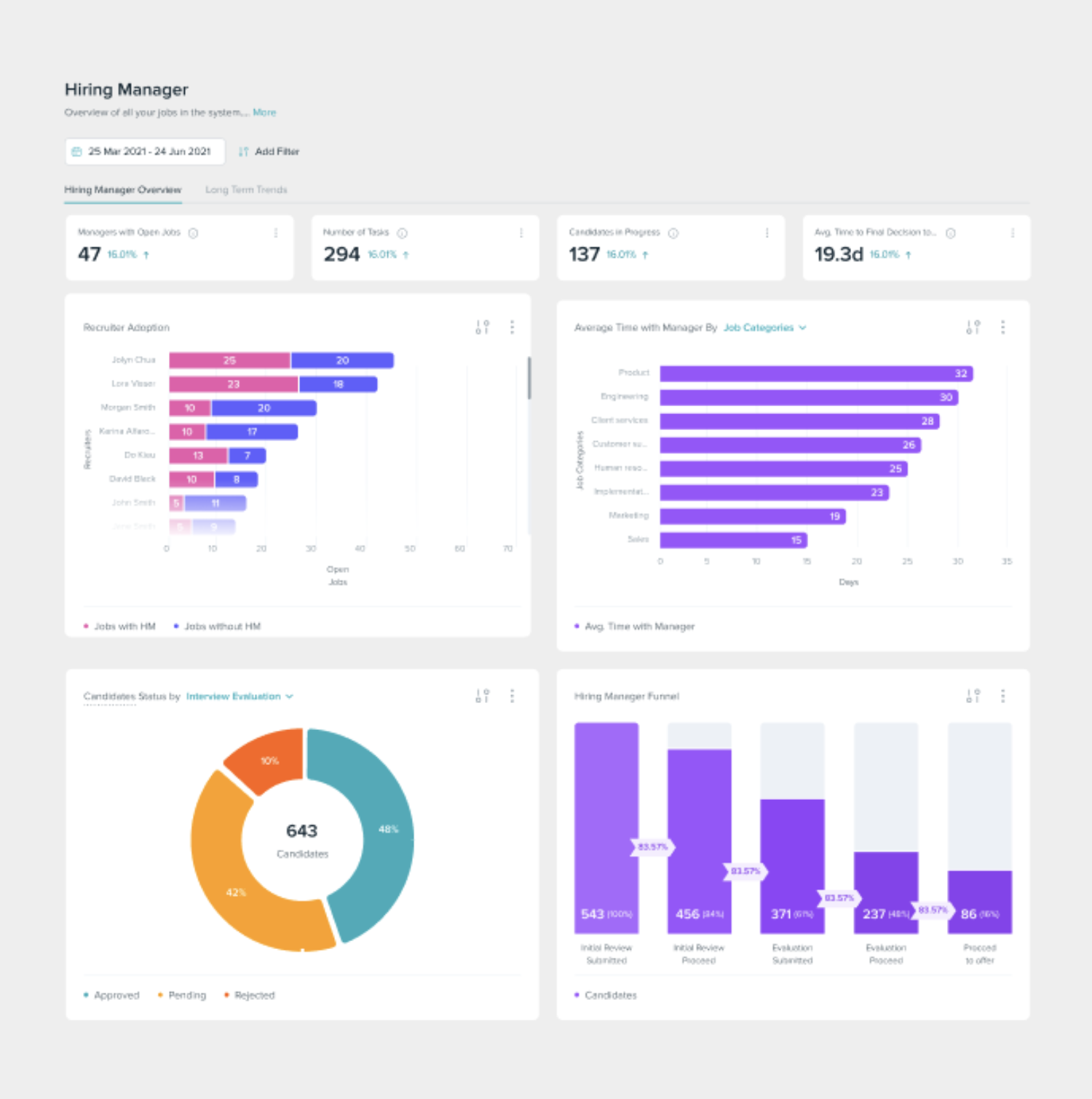
Dashboard of Phenom Platform. (Source: Phenom)
The new system collects several data sources on employees, including:
- The employee’s strengths
- The employee’s skills
- Duration in the employee’s current
- Desire an employee has for future growth at the company
As a result, the system can provide recommendations that align with an employee’s interests and qualifications.
The system has resulted in a few main benefits. It’s much easier for internal recruiters to find employees for open roles. After the shift to the new system was complete, Cigna filled 65% of their roles internally.
Making Preliminary Diagnoses
Minimizing the risk of infection when pursuing medical care became a priority at the onset of COVID. Telehealth minimized that risk. Before the pandemic, Cigna had already begun integrating virtual care with in-person services.
Cigna worked with Infermedica to develop a symptom-checking app capable of:
- Making preliminary diagnoses
- Acting as a triage tool
They launched a pilot for the online Symptom Checker they developed in partnership with Infermedica, a leader in developing AI tools that enable triage and preliminary medical diagnoses. The app helps patients by equipping them with information before they physically come in for a consultation. Since its launch, Infermedica’s Symptom Checker is now known as Infermedica Triage.
According to the vendor’s website, their medical guidance platform provides the following benefits:
- Reduced provider burnout
- Optimized costs
- Allows telehealth services to provide a more personalized patient experience
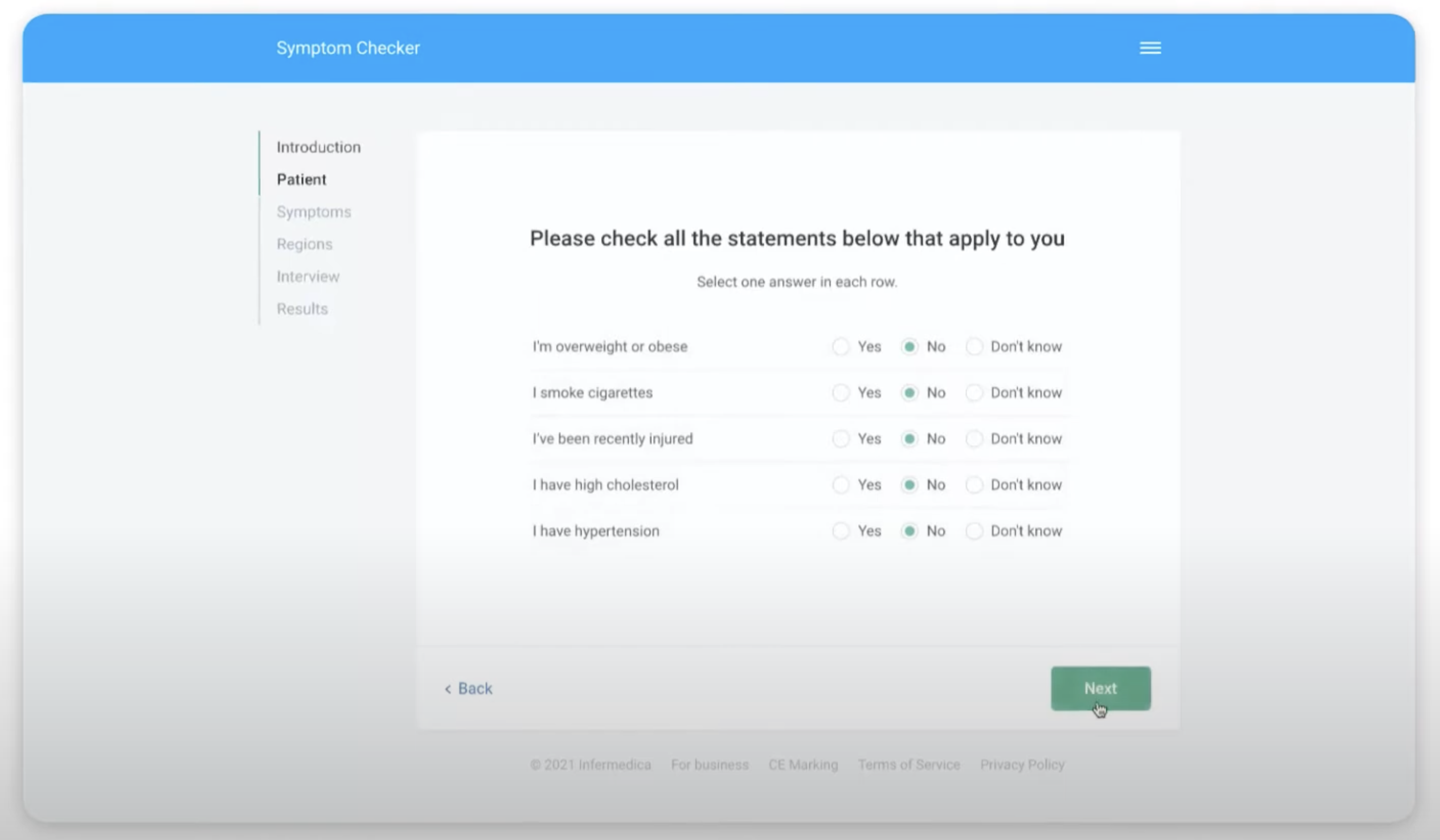
Patients use the app ahead of an appointment and self-report their symptoms. In the first step, the symptoms, patient demographic data, and risk factors are analyzed. Next, the inference engine uses probabilistic modeling to make appropriate recommendations.
Infermedica’s Symptom Checker. (Source: Infermedica)
Screenshot Showing Quantitative Benefits of Infermedica Triage. (Source: Infermedica)
Based on currently available information, it’s not clear what quantifiable improvements Cigna has experienced based on their partnership with Infermedica. However, several case studies featuring three of Infermedica’s partners have demonstrated the following, respectively:
- 39% increase in operational efficiency through pre-visit interviews.
- 106% increase in self-care after checking symptoms online.
- 75% increase in retention to use telemedicine vs. in-person.