Cardinal Health is a global healthcare services company with a rich history and a strong focus on providing integrated solutions to the healthcare industry. Established in 1971, the company has become a leading player in the healthcare sector, offering a wide range of products, services, and technologies to enhance patient care, optimize supply chain efficiency, and drive value-based outcomes.
Serving 90 percent of the US hospitals and employing over 4400 people globally, the company generated a record-high revenue of 181 billion US dollars in FY 2022, up from 162 billion in FY 2021.
Cardinal Health is also at the forefront of adopting cutting-edge technologies like AI to enhance its services further. Through its strategic investments in AI-powered solutions with IBM, Google Cloud, and many more vendors, the company aims to optimize supply chain logistics, improve patient care with predictive analytics, and enhance operational efficiency.
In this article, we will examine two use cases showing how AI initiatives currently support Cardinal Health’s business goals:
- Improving patient outcomes: Analyzing Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) with machine learning to reduce costs and enhance quality of life through personalized care plans and risk management.
- AI-powered virtual assistant to reduce costs and enhance agent efficiency: Deploying conversational AI capabilities to create a customer-facing intelligent assistant, helping the company save costs and increase efficiency.
Use Case # 1: Improving Patient Outcomes
In the healthcare industry, patient outcomes are not solely determined by medical treatments. Social Determinants of Health (SDoH), including factors like economic stability, education, access to transportation, and quality healthcare, also significantly impact patients’ overall well-being.
However, as mentioned in the press release by Cardinal Health, physicians often need more training and tools to analyze SDoH data effectively, leading to these vital factors being overlooked in clinical decision-making. This omission can result in suboptimal patient care and an increased risk of adverse outcomes.
Cardinal Health partnered with Jvion, a clinical AI developer, to address this critical challenge to integrate Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning into their NavistaTM TS platform. The collaboration resulted in Jvion CORETM, a decision support tool that analyzes clinical and socioeconomic data.
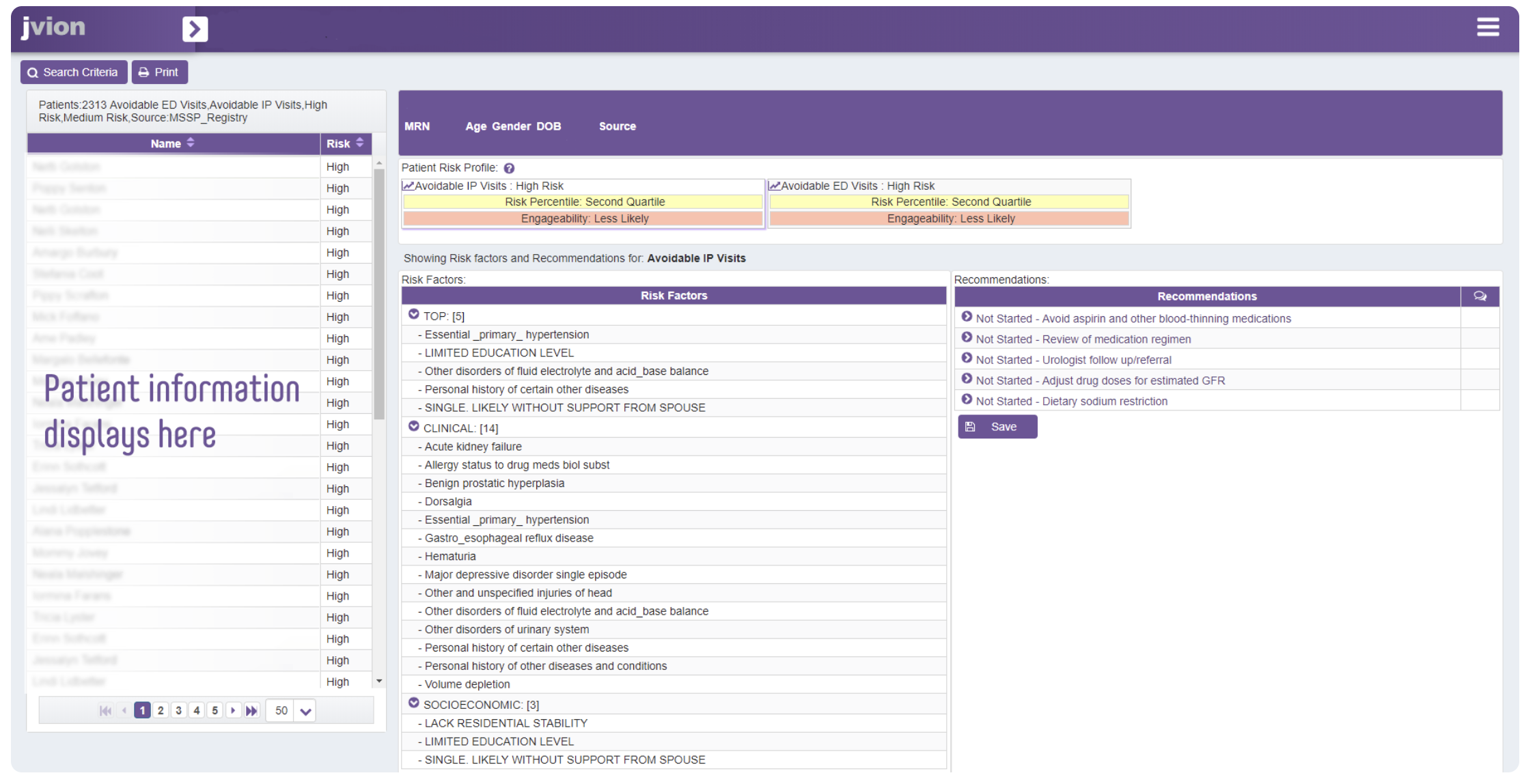
Jvion Software’s standard interface for patient profiles. (Source: Software Advice)
Jvion CORETM harnesses the power of AI and machine learning algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data. It integrates healthcare providers’ electronic health records (EHRs) with external data from various public and private sources, including the US Census Bureau, the Department of Housing and Urban Development and medical records.
By merging these data sets, the tool provides a comprehensive view of patients’ health risks, enabling it to identify high-risk SDoH profiles that might negatively impact patient treatment outcomes. The integration of AI-driven insights through Jvion CORETM offers several benefits to healthcare providers:
Holistic Patient Care: The tool enables providers to assess patient health comprehensively by considering medical conditions and social factors. This holistic approach allows for more accurate risk assessments and personalized care plans.
Proactive Risk Management: By identifying patients at higher risk of health deterioration, mental health crises, emergency department visits, and hospitalizations, providers can take proactive measures to prevent adverse events and improve patient outcomes.
Enhanced Decision-Making: AI-driven insights complement traditional clinical profiles, giving providers a deeper understanding of each patient’s unique circumstances. This information empowers them to make better-informed decisions and tailor treatments accordingly.
Cost Reduction: Identifying and mitigating health risks before they escalate can lead to a decline in unplanned hospital admissions, resulting in cost savings for both patients and healthcare institutions.
Improved Quality of Life: The tool’s ability to predict health deterioration and increase referrals to palliative care ensures that patients with life-threatening illnesses receive appropriate care focused on enhancing their quality of life.
As claimed in the press release, Cardinal Health observed these results in oncology practices:
- 12.3% decline in unplanned hospital admissions
- 271% increase in depression screenings
- 111% increase in referrals of patients to palliative care – the kind of care focused on improving the quality of life for patients with life-threatening illnesses.
Use Case # 2: AI-Powered Virtual Assistant to Reduce Costs and Enhance Agent Efficiency
When the COVID-19 pandemic first struck, like any other healthcare company, Cardinal Health also faced the same challenges as many brick-and-mortar businesses, including call centers. Hospital admissions fell dramatically in March 2020, and many hospitals reported operating at less than 50 percent capacity. Given the unprecedented environment, the company sought to improve customer experiences while ensuring business continuity and responsive agent support.
According to a case study report by IBM Cardinal Health’s Director of Augmented Intelligence, Jasmeet Singh, spearheaded an AI initiative in 2019 using Watson Assistant to help their IT agents troubleshoot IT issues efficiently.
Challenges with virtual assistants occur when they need help comprehending the number of tasks to perform together. While humans think and say in words, computers only work with zeros and ones – and often, natural language processing (NLP) helps to bridge the gap.
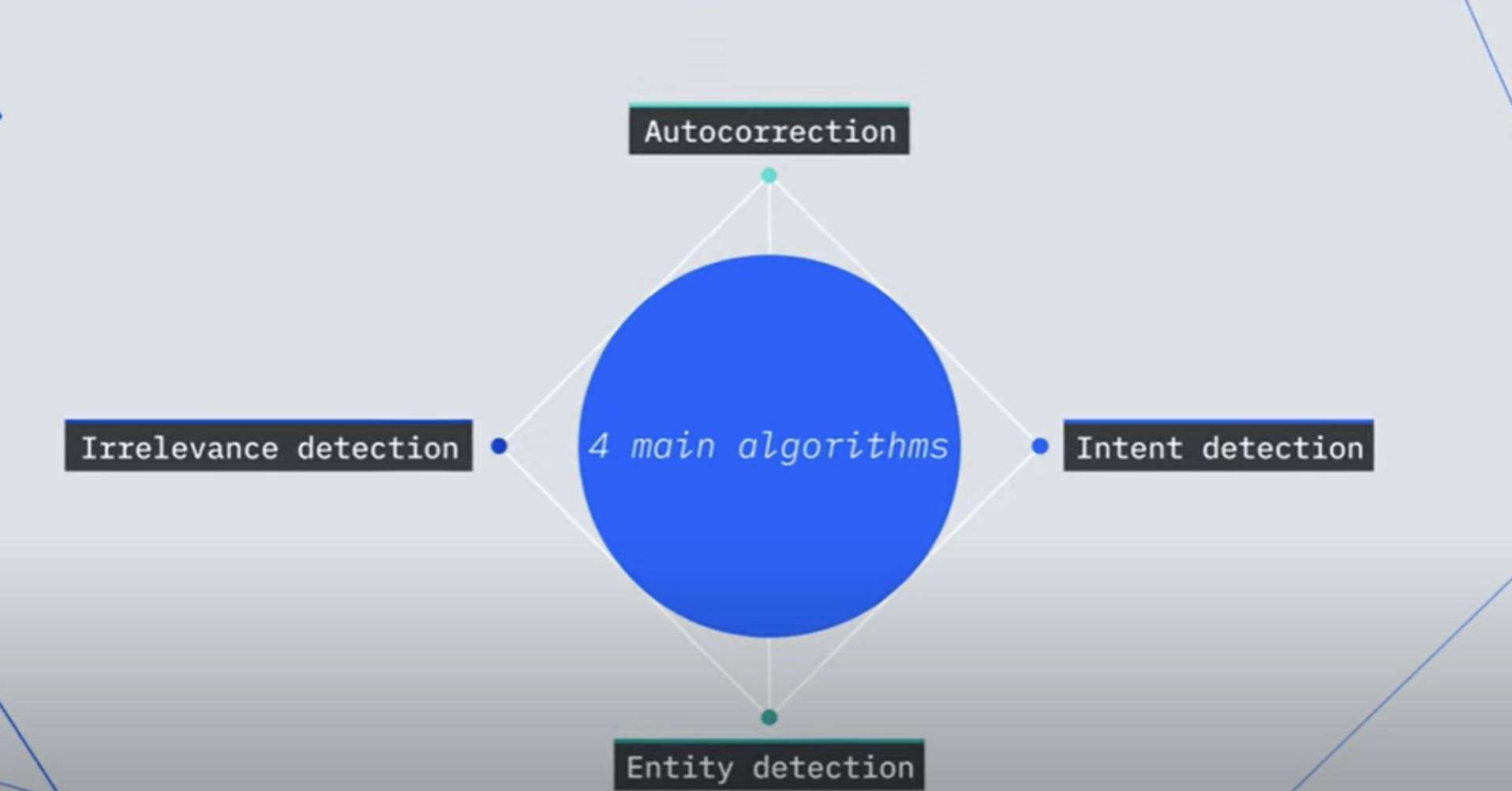
As IBM reports in the video, with Watson Assistant, four main algorithms work behind the scenes:
- Intent detection
- Entity detection
- Irrelevance detection
- Auto correction
Screenshot from – Behind the Algorithm – IBM Watson Assistant Explained. (Source: IBM)
For a password change, a customer may say he needs help with login forgot their password, or may ask to reset their password. While the commands are different, the intent behind them is the same. Leveraging NLP and machine learning, Watson Assistant can detect the customer’s specific intent in regards to their password and takes the following action.
Phrases like ‘What time do you open?’ are taken by Watson as keywords and then processed to take action and answer the question. Often, frustrated customers get angry and use obscenities, so the algorithm prioritizes what communications signal the customer’s true intent and can redirect the conversation to the most relevant category to assure customer outcomes based on previous uses.
The video below is approximately three and a half minutes long and explains how Watson can be trained specifically to the use case according to the company’s needs.
Before COVID-19, nurses relied on manual fever checks for patients. However, when the pandemic emerged, this approach became challenging due to the virus’s nature. Recognizing the need for innovation, some companies saw this as an opportunity to develop and deploy AI solutions.
These technologies utilized thermal scanning to screen a large number of patients for elevated temperatures while also detecting additional symptoms such as skin discoloration and excessive sweating.
Cardinal Health previously set up a call center to help its employees in troubleshooting IT issues, which was forced to shut down because of COVID. As the case study report claims, since the company already had leveraged IBM Watson, they were able to scale up and help their agents rapidly troubleshoot IT issues.
Hence, to free up human agents for more complex tasks, Cardinal Health applied AI to create a customer-facing agent CHIA (Cardinal Health Intelligent Assistant).
CHIA answered queries about medical products and medicine shipments, delivering satisfactory resolutions in under two minutes. The team re-engineered the existing solution to create CHIA, utilizing 80% of the original code for rapid deployment.
The healthcare company claims to have observed:
- Improved Customer Experience: CHIA’s quick and accurate responses helped customers promptly get the information they needed, enhancing their overall experience.
- Cost Reduction: The AI-powered virtual assistant handled call volumes independently, eliminating the need to allocate live agents for these routine inquiries, leading to cost savings.
- Business Continuity: Despite the challenges posed by the pandemic, Cardinal Health’s AI initiatives ensured continued customer support and operational efficiency.
- Scalability: Cardinal Health’s “Think big, start small, scale fast” approach allowed them to expand their AI initiatives from internal use to customer-facing applications.
- Enhanced Efficiency: By automating routine tasks, the AI initiatives enabled human agents to focus on more complex issues, improving overall team productivity.
However, neither IBM nor Cardinal Health offers any tangible numbers or specific metrics in these results publicly.