
Amazon is the largest online retailer in the world by market cap. Founded in 1994 in Seattle, Washington, as a book-selling platform, Amazon has become a household name offering a wide variety of products and services. As of 2020, online retail product sales account for most of the company’s net revenues, followed by third-party retail seller services, Amazon Web Services, and subscription services.
Today, the company boasts mature AI applications across eCommerce, logistics, warehousing, and more. Amazon claims to be driven by four principles, the first being “customer obsession rather than competitor focus.”
In an interview with Internet Association, Jeff Bezos – Founder and Executive Chairman of Amazon – summarized these efforts, emphasizing that, in addition to the AI applications that the company uses and analysts can readily see, the vast majority of Amazon’s AI investments happen behind the scenes:
A lot of the value we’re actually getting from machine learning is actually happening beneath the surface, and it is things like improved search results, improved product recommendations for customers, improved forecasting for inventory management, and literally hundreds of other things beneath the surface.
In this article, we explore two of Amazon’s current AI use-cases in its eCommerce business:
- Personalized Product Recommendations – the science behind Amazon’s product recommendation algorithm and how it is integrated into almost every part of the purchasing process from product discovery to checkout.
- Alexa-Enabled Voice Shopping – how Amazon has enabled a hands-free shopping experience by training Alexa to better interpret and predict customer needs.
We’ll begin by covering Amazon’s product recommendations in greater depth to illustrate the development and improvement of its recommendation algorithm over time and its business impact and ROI.
Personalized Product Recommendations
Amazon offers personalized product recommendations as a marketing technique that enables the company to continue to win a more significant market share and continue satisfying customers by accurately anticipating their needs through personalized product recommendations. To power their recommendation algorithm, Amazon uses item-to-item collaborative filtering.
According to a report by researchers who worked on Amazon’s recommendation algorithm, the algorithm works by matching each user’s previous purchases to similar products. It then compiles these similar products into a recommendation list for each user. The idea is to create recommendations that more closely align with what the user is likely to buy than recommendations generated using purchases by other similar customers.
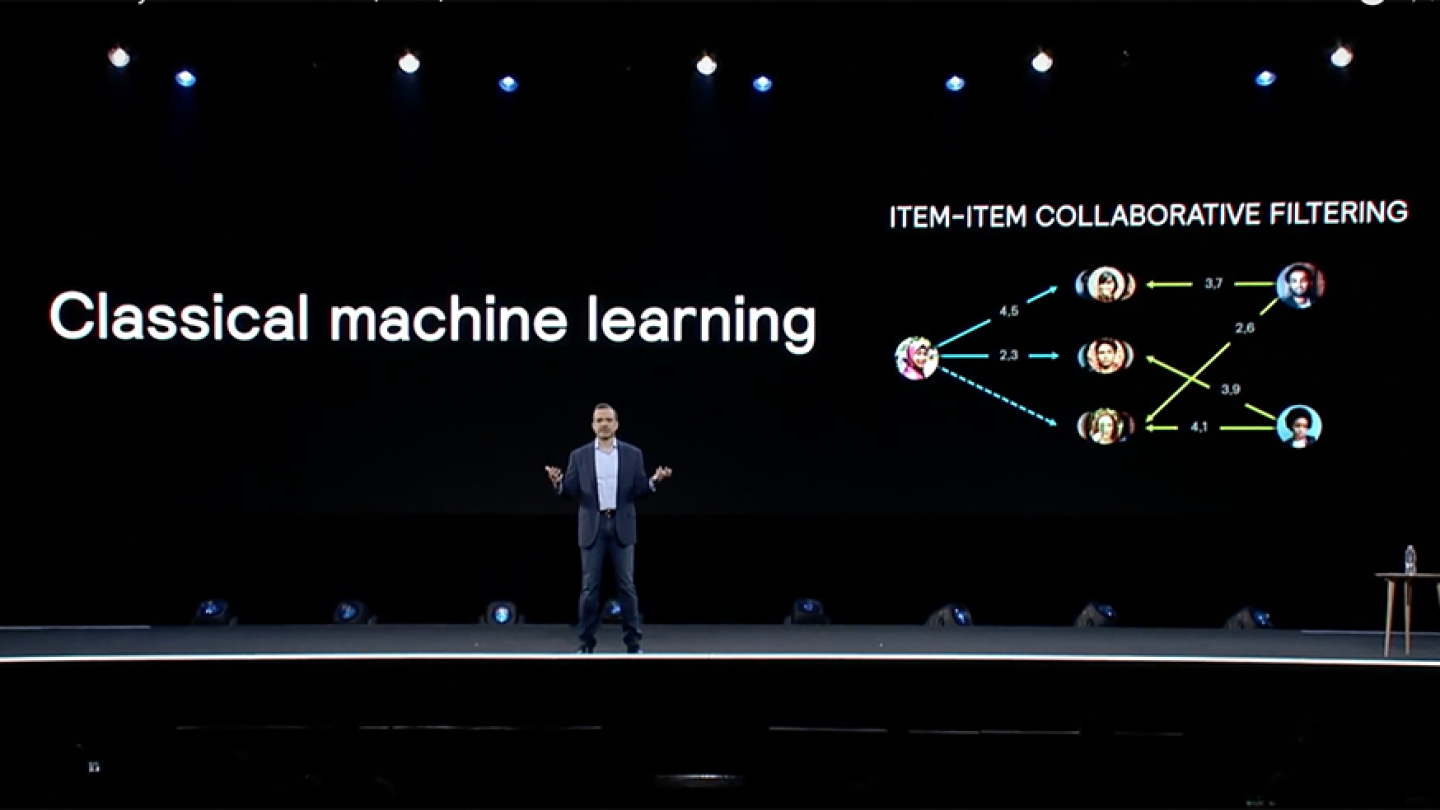
Below is a video of a 2019 keynote presentation done by Jeff Wilke, Amazon’s former Consumer Worldwide CEO, focusing on developing and improving their recommendation algorithm.
From the moment a customer signs in, they will be presented with various recommendation headers. When they click on one of these headers, such as “Recommended for You,” they will be taken to another page where their personalized product recommendations are listed and can be filtered by various criteria, including product type, customer reviews, and more.
This is just one of many examples of how customers are presented with recommendations on Amazon’s mobile application, website, and even emails.
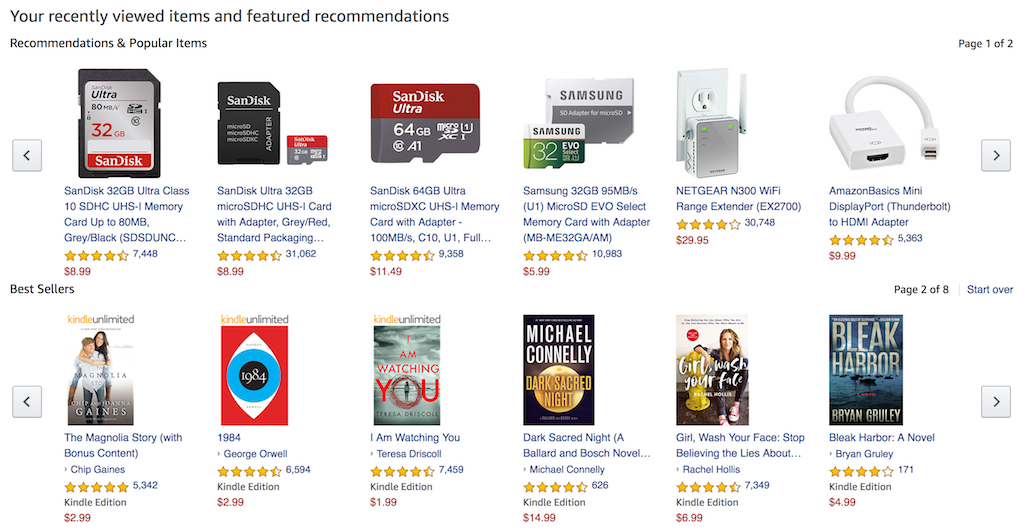
A 2013 McKinsey & Company report claimed that personalized recommendations drove 35 percent of purchases on Amazon. However, our secondary research could not confirm this statistic with any statements or data released by Amazon themselves. Yet, the business value for this application is clear: it aims to improve the user experience when shopping on Amazon, which could potentially improve the loyalty and lifetime value of users.
Alexa-Enabled Voice Shopping
Amazon claims that its voice assistant Alexa allows users to find and purchase products and walk through the checkout flow with voice prompts instead of clicking or tapping a screen. This, according to Amazon, allows customers to control their checkout experience hands-free.
Overall, this AI application aims to increase convenience for customers shopping on Amazon, from creating a shopping list to getting recommendations from Alexa. For Amazon, this investment in AI enables the company to attempt to further solidify its place in the market by maintaining an edge in providing convenience for consumers. Amazon explains how Alexa works in general, stating that:
[Alexa-enabled] devices use built-in technology that matches what you’ve said to the acoustic patterns of the wake word… When the device detects the wake word, it sends your request to Amazon’s secure cloud, where the cloud’s more powerful capabilities verify the wake word as your request is being processed. After confirmation, an answer to your request is sent back to you. For example, when you say, “Alexa, play top hits from Amazon Music,” we use the recording of your request and information from Amazon Music to play top hits for you on your device.
In a 2018 paper, Amazon researchers discussed Alexa’s capabilities with the launch of new Alexa-enabled devices. They explained that one of the ways the Alexa team trains the neural networks is with a “voice-only model” that identifies and sorts utterances based on two parameters they refer to as “intent and slot.” Intent relates to the action the customer wants Alexa to perform, and the slot gives the model more details about intent.
For example, if a customer asked an Alexa-enabled device to play Harry Potter, the identified intent would be “play” relating to a movie. In contrast, the slot value would identify “Harry Potter” as the movie’s name that the customer would like the Alexa-enabled device to play.
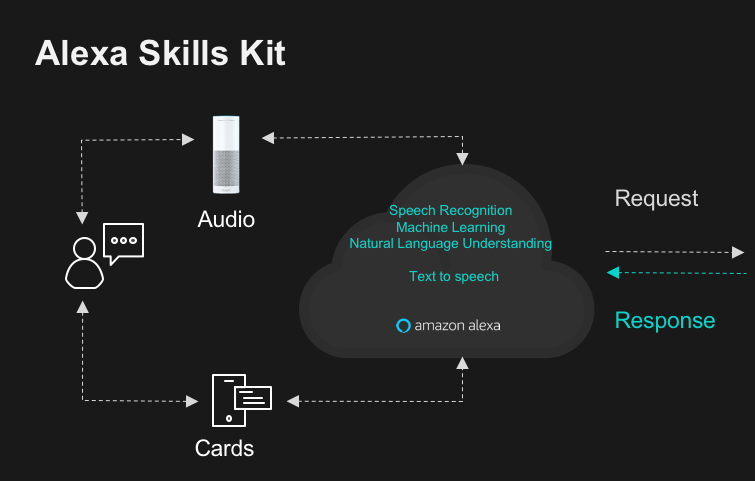
The machine learning process behind Alexa-enabled voice shopping is similar. The user can activate Alexa and begin listing items they would like to search for, buy, or add to their shopping list. When items are added to a customer’s shopping list through Alexa voice shopping, they can access a text version of this list in their Alexa app and make changes later.
Below is a short video from Amazon further explaining and demonstrating how Alexa voice shopping works:
Amazon states that users can activate voice shopping with Alexa through their Alexa-enabled devices, such as the Echo, Amazon Fire TV Cube, Echo Dot, and more. The company also claims that Alexa helps users by suggesting the types of products they frequently purchase or recommending “Amazon’s Choice” labeled products if they search for an item they’ve never purchased before.
Since its initial release in 2014, more than 100 million Alexa-enabled products have been sold worldwide, according to Amazon’s Senior Vice President of Devices and Services, David Limp, in a 2018 interview. Despite this claim, we were unable to find any statements from the company relating to the growth rate of Alexa-enabled product purchases as of 2021 in our secondary research.







