The K-12 online tutoring market is a growing sector and is projected by market research firm Technavio to reach $120.67 billion by 2021. Growing numbers of students are taking college entrance exams such as the SAT and tutoring industry giants such as Khan Academy are helping students meet their test prep goals.
However, personalization of the online tutoring experience has not been fully adopted across platforms. Today, artificial intelligence is beginning to help shape this approach.
In this article we explore examples of tutoring platforms which integrate AI. We cover three major categories of tutoring applications that should be of interest to business leaders in the education space:
- Chatbots as Tutors and Teachers
- Machine Learning for Educational Data Analytics and Quality Monitoring
- Machine Learning for Matching Tutors with Students
For each application we provide a company overview, explanation of how the platform functions and outcome data and/or results where available. Each example is organized under a sub-heading which serves as a quick reference when navigating through the article.
(This article will focus exclusively on AI applied to virtual learning and tutoring. Readers interested in a general exploration of AI in Education may find our more broad article “Examples of Artificial Intelligence in Education” to be an informative read.)
Chatbots
Duolingo – Chatbot for Learning Foreign Languages
In October 2016, Duolingo officially announced the release of three iPhone compatible chatbots designed to help foreign language learners gain fluency and confidence in speaking in French, Spanish and Italian.
Consistent with traditional bots, users interact with the app though prompts using natural language. However, the company claims its chatbot is more unique due to its ability to “accept and react to thousands of unique responses” instead of a more limited range of prompts.
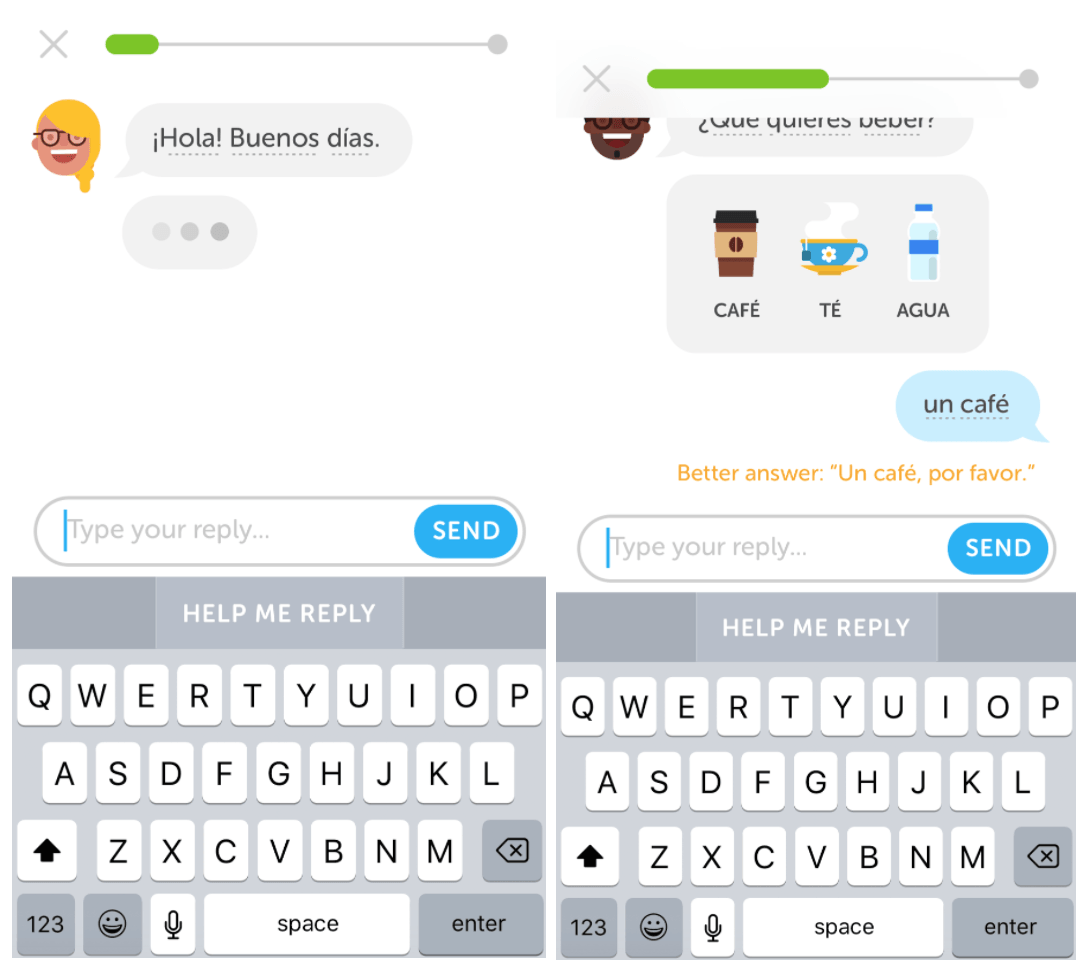
Features include a “help me reply” option that provides users with suggested responses if he or she is ever unsure how to respond during a language chat. Unfamiliar words can also be clicked on for realtime translations or pronunciations during chats.
The company claims it has always used machine learning to help personalize each lesson delivered through its platform. Specific examples include:
- Determining which sentences will help a user best improve his or her weakest language skills
- Recommending immersion practice documents (translations) based on a user’s progress
- Estimating the quality of a translation-in-progress
To date, the company reports that it services over 150 million users. An independent research study conducted by Roumen Vesselinov, PhD and John Grego, PhD on the effectiveness of Duolingo for learning Spanish suggests that the platform is an effective tool.
The same research team has conducted a series of effectiveness studies on competing language software programs including Babbel and Rosetta Stone. The impact of Duolingo’s chatbots (on engagement, revenue, learning outcomes, etc) has yet to be reported.
EdTech Foundry – Chatbot Acts As Teaching Assistant
EdTech Foundry, a Norway-based tech company has recently released Differ, a chatbot designed to assist students in higher education. The system is designed to provide quick answers to student questions that tend to recur each semester.
According to the company’s website, questions range from general administrative questions to more detailed questions about syllabi and course work expectations. In addition to answering questions, the chatbot occasionally suggests academic articles and further reading to students that pertain to their coursework. The chatbot also suggests direct ways that a student can contribute to their class such as posting in forums.
In the short video below, Kristian Collin Berge, EdTech Foundry CEO, discusses how he used the Differ chatbot to as a teaching assistant in his classroom to increase student engagement:
To function, the chatbot uses algorithms and must accumulate and process student questions and student-teacher activity over time to improve its ability to make useful recommendations. The company claims that its pilot program results demonstrated five times higher student engagement on messages posted by a bot as compared to a human teacher.
Contrary to some concerns about how technology can affect a student’s experience with course work Bill Gates is among proponents of the technology. He suggests chatbots have great potential for achieving increased student engagement because of how they are designed to communicate with their users.
While we’ve covered the chatbot efforts of Google and Facebook in relative depth, education is – admittedly – a rather new use-case without the budget or the conversational volume of the world’s big tech giants. We hope that the use-cases and open source technologies from leading tech companies will increasingly make their way into education and other less funded domains. Time will tell.
Machine Learning for Data Analytics and Quality Monitoring
Thirdspace Learning – AI Used for Feedback on Math Tutoring Instruction
Founded in 2012, Thirdspace Learning is self-described as the largest one-on-one online math tutoring platform in the U.K. As of 2016, the company is reportedly integrating artificial intelligence into its operations. The purpose is to better track student progress and to optimize its services. While a specific timeline has not been reported, the company aims to provide its online tutors with feedback on their tutoring performance in real-time using artificial intelligence.
For example, if a student misunderstands a concept or if a tutor skips an important step, Thirdspace wants AI to identify the gaps and alert the tutor before the issue progresses.
On the data collection front, company founder Tom Hopper has stated that the ThirdSpace Learning records every tutoring session amounting to thousands of hours every week. To provide additional context, according to the company’s website, over 400 math specialists have been recruited and trained and over 100,000 hours of math tutoring has been delivered to date.
Robust data collection improves the ability of an algorithm to “learn” the parameters of a data set and enables it to make better recommendations. It is plausible that Thirdspace is aiming to increase its data to lay a solid foundation for its AI implementation efforts. This would be particularly applicable to understanding student learning styles and tailoring math tutoring in an increasingly personalized way.
Thinkster Math – AI Used for Feedback on Math Tutoring Instruction
Thinkster is a math tutoring platform that integrates artificial intelligence and machine learning to help math coaches track student performance. According to its website, Thinkster uses AI to help visualize a student’s thought process as he or she works on a math problem.
The tutoring platform records student work and tracks the steps a student chose to solve a math problem. As a result, math coaches can identify problem areas and inform strategies for improving student performance. The objective is to personalize each student’s learning experience based on performance data.
For example, consider a word problem involving 3 apples, 4 oranges and 5 carrots and a student is asked to calculate the total amount of fruit. Thinkster’s curriculum is designed to include “conceptually unrelated numbers (or distractors).” In this example the 5 carrots would be the distractor. The platform would track the student’s ability to solve similar problems which include distractors to achieve overall skill mastery in this area.
The 3 minute video below provides a succinct overview of the Thinkster platform featuring a simulated walk-through of a student using the platform and how Thinkster records and analyzes the student’s performance:
The details of how AI and machine learning are specifically impacting the business model are not clearly discernible from the company’s website or Linkedin page.
iTalk2Learn: Machine Learning Used for Fraction Solutions
iTalk2Learn is an online math tutorial system designed for elementary students. A collaborative project developed in Europe, the system developers claim machine learning is used to structure personalized lesson plans.
The program focuses extensively on fractions, which according to the developers, remain a barrier to progression in the study of mathematics for a disproportionate number of students. The program’s Fractions Lab reportedly emphasizes visual representations of fractions and real-world application of fraction concepts. Through the use of its seven modalities, the program claims to balance structured activities with interactive, practice-based work.
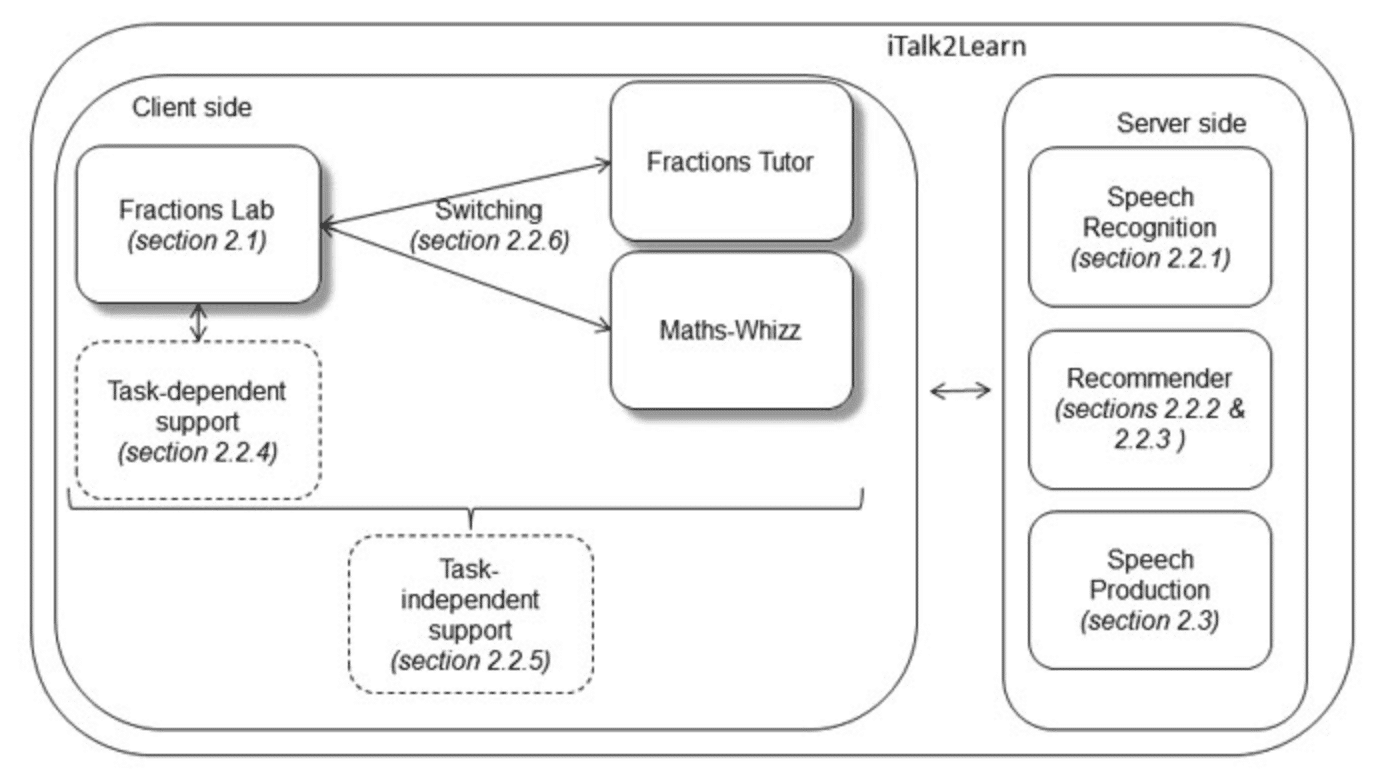
The program model incorporates features such as speech recognition. The machine learning technology is currently calibrated for English users only. Currently in a trial phase, students were recorded while solving problems involving fractions. The developers are analyzing transcripts from these recordings to “teach” the system to recognize common questions and speech patterns. The company claims that a German speech recognition iTalk2Learn is in the works.
As a machine learning based program, the developers of iTalk2Learn emphasize real-time analysis of their users’ experiences and results. For example, this would be achieved by monitoring how a student solves a problem involving fractions and providing feedback specific to that student’s approach. Mostly through anecdotal reports from some teachers, the company claims instances of higher student engagement and confidence in fraction work in “certain classrooms.”
Matching Tutors with Students
Brainly – Machine Learning Used to Match Student Problems with Content Experts
Brainly is a global online learning community where students can post academic questions and community members can offer solutions. The platform is reportedly using machine learning algorithms to match problems with content experts. Human moderators are content specialists who provide oversight and monitor the quality of solutions provided by community members.
This 1 minute video below provides an overview of how the Brainly online learning community works:
Brainly aims to personalize each user experience and minimize low quality content. This is an important feature of the learning community’s brand but also an ambitious task. According to its website, Brainly receives 80 million unique visitors each month across over 35 countries.
“The whole point of Brainly is to use data and technology to focus the attention on a very precise and specific problem. So Amazon, for instance, wants you to look at more and more stuff and to do things in quantity. But Brainly wants to do the opposite. We want to use machine learning to create a fully personalized learning path, to identify precisely where a student is stuck or confused or unclear, then hone in on that one specific problem and find a solution.” -Professor Chirag Shah of Rutgers University, (March 2017)
The company has partnered with professionals with experience in AI and machine learning such as Chirag Shah, Ph.D. of Rutgers University to help achieve its goals.
MyTutor – Algorithm Used to Match Students With an Ideal Tutor
In collaboration with University College London’s (UCL) Institute of Education, the online tutoring site MyTutor, has reportedly developed an AI-powered system to streamline the process of connecting students to their ideal tutor.
After signing up, a prospective student is prompted with a series of questions pertaining to his or her personality type. The collected responses are processed using an algorithm that matches students to tutors based on compatibility. Examples of compatibility parameters include creativity, logical thinking and confidence. The system can then use these descriptors to automate the interview process and complete a match. CEO James Grant has stated that the program is founded on the idea that a complementary dynamic between students and their teacher is integral to academic success.
The short 1:11 minute video below demonstrates MyTutor in action:
One professor suggests that a limited understanding of the technology behind MyTutor’s platform may lead some parents to become concerned about providing details about their child’s personality online. Despite these challenges MyTutor claims that it has achieved a 93 percent success rate with users and boasts an average of five stars from its 43,000 user ratings.
Concluding Thoughts
AI is steadily being introduced into the online tutoring experience and is providing methods personalization and improving the quality of services delivered through data analytics. Despite the deluge of chatbots entering the market across industries, tutoring bots may have a promising future in the coming years (though we’re far from achieving human level sophistication in chatbots any time soon).
Bots in the smart virtual learning sphere are subject to a greater degree of consistent utilization and learning opportunities compared to other industries which may receive occasional traffic. Personalization of the learning experience is a general theme across applications.
Another important theme to highlight is integration of AI and human interaction. Smart virtual learning platforms do not appear to be aiming for AI to replace human instruction but rather to supplement and enhance the human-to-human experience. A 2016 report published by Pearson on AI in education complements our observations and advocates for wider adoption of AI at scale:
“Drawing on the power of both human and artificial intelligence, we will lessen achievement gaps, address teacher retention and development, and equip parents to better support their children’s (and their own) learning. Importantly, doing this will require much more than borrowing the language of AI – we need to go deep, harnessing the power of genuine AIEd, and then working to apply it in real-life contexts at scale.” – Intelligence Unleashed: An Argument for AI in Education
Similarly, a 2016 report on education published by the World Economic Forum suggests that machine learning is among the technological advances which have strong potential for personalizing instruction and improving social and emotional learning. The National Education Association is among advocates of developing social and emotional skills for improving student outcomes:
“Social and emotional skills are critical to being a good student, citizen, and worker. Workforce demands aside, many call for the 21st century classroom to be student-centered and to support individual learning needs. Moreover, students’ ability to learn well depends not just on instruction, but also on factors such as the school climate, a sense of belonging with peers, positive relationships with educators, and the feedback they receive.” – The National Education Association
As more students access smart virtual learning tools, machine learning has the potential to become increasingly useful to handle the large amount of data and to provide tutors with constructive feedback. Quality monitoring is always critical when providing academic support and this will become more apparent as the market becomes increasingly competitive.
Header image credit: PKHS Schools




















