The company that would become eBay was founded as a sole proprietorship under the name AuctionWeb in September 1995 by Pierre Omidyar. The company changed its name to eBay in September 1997. The company reports selling just over $7 million in goods before being a California-registered corporation in May 1996.
Today, eBay is a global e-commerce leader in more than 190 markets throughout the world. In its 2021 annual report, eBay reported over $10 billion in revenue and claimed 147 million buyers worldwide. As of May 2022, eBay trades on the Nasdaq exchange (symbol: EBAY) and has an approximate market cap of approximately $26 billion.
In this article, we’ll examine the deployed applications of AI at eBay through two discrete use cases:
- Enhanced Product Classification – eBay uses text and image similarity models for more accurate and scalable product classification.
- Image Processing – eBay uses computer vision and image processing AI to enable users to remove backgrounds in item photos.
First, we’ll discuss how eBay uses machine learning modeling for more enhanced product classification.
Enhanced Product Classification
In e-commerce, an accurate and fast product classification system is paramount to the buyer, seller, and selling platform – in this case, eBay. For the company, better product classifications result in more relevant and personalized product recommendations, often leading to higher customer satisfaction and more sales.
Conversion rates, as well as scalability and speed of product classification operations, are critically important to a company the size of eBay. Two essential elements of product classification are text similarity and image similarity. Similarity algorithms calculate the degree of likeness between two objects.
Dr. Selcuk Kopru, head of machine learning and natural language processing at eBay, talks about the importance of scalability:
“To build a marketplace that scales and performs well, it is important to [put into production] a lot of AI capabilities, and similarity is one of the most practical tools.”
In the following video, Dr. Kopru discusses the significance of similarity algorithms for eBay:
To make the platform more scalable and efficient – and help eBay achieve its sales goals – the company claims that it devised and implemented an AI model that includes algorithmic elements such as similarity clustering, cosine similarity vectoring, and indexing.
eBay claims it used two key similarity measures in its AI model: text similarity and image similarity. Text similarity works by determining how “close” two texts are in terms of lexical and semantic similarity on a vector. Similarity metrics used to compute a similarity score are node similarity and K-nearest neighbors, both of which are calculated in eBay’s model per Dr. Kopru.
To illustrate how this works, Dr. Gupta demonstrates by typing in the name of an espresso maker, “Breville 87,” into eBay’s search engine. The text similarity algorithm, represented in the form of a 2-dimensional vector, produces the following result:
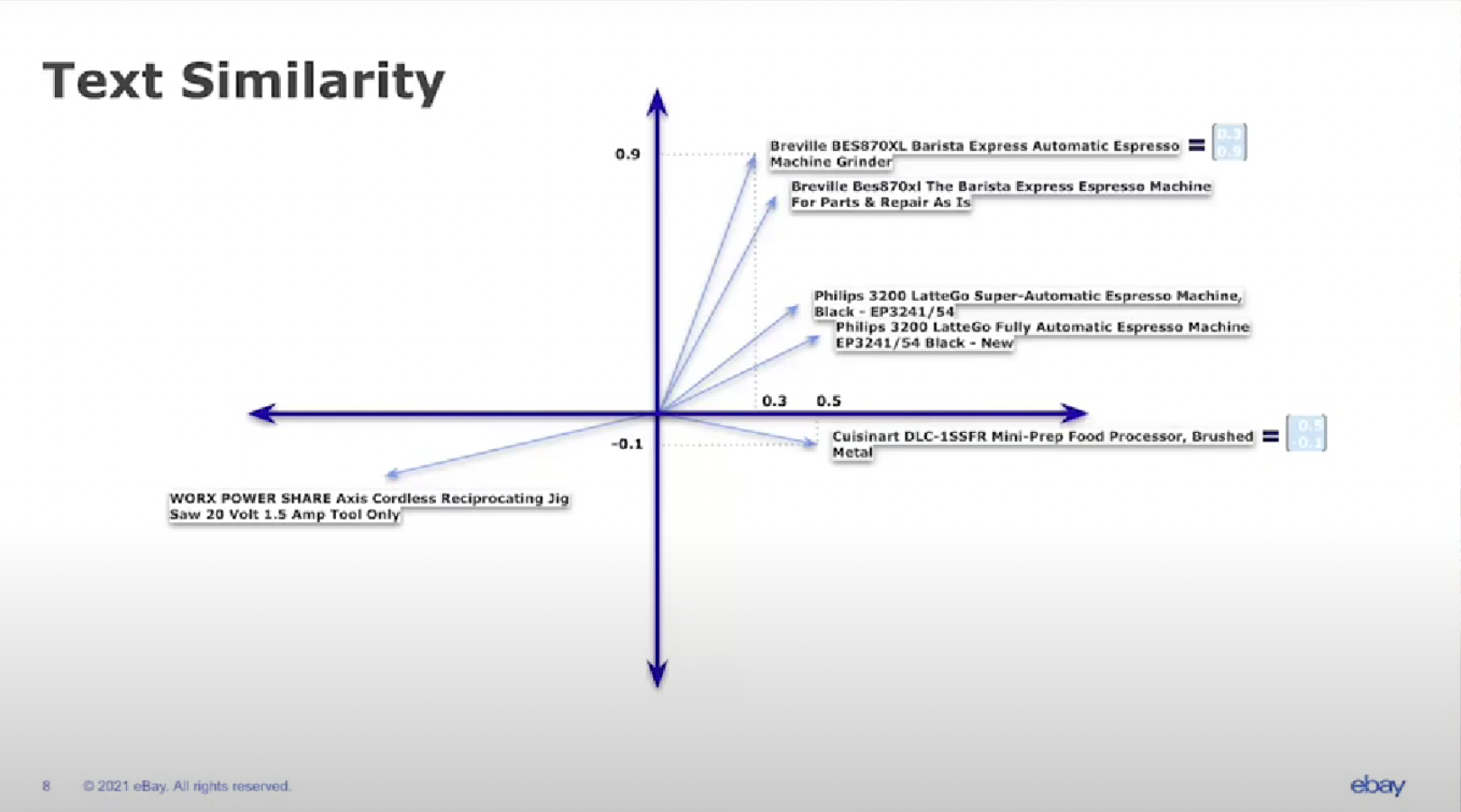
Source: eBay
The search for “Breville 87” as an image vector:
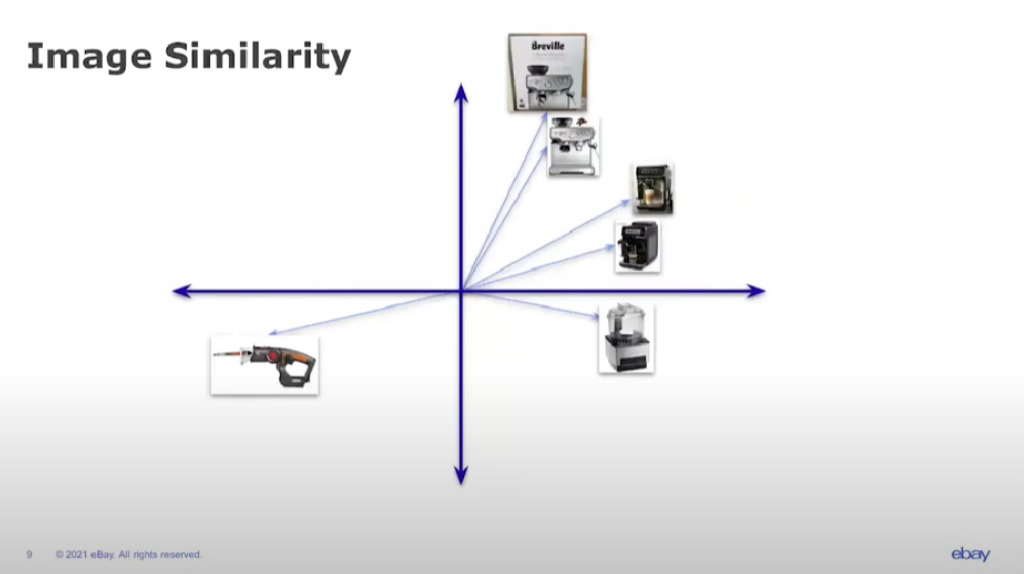
Source: eBay
Dr. Kopru claims that the benefits of accurate text similarity algorithms include better search results, identification and removal of duplicate items, and differentiation between text types (e.g., the item title as opposed to the item description.) Potential benefits of an accurate image similarity algorithm are removal or recategorization of products with poor title or description-image match and enhanced image search.
Regarding tangible business results of eBay’s AI model, the company claims that implementing similarity algorithms has resulted in a 2.14% increase in peak transaction rate (PTR).
Image Processing
eBay claims that users depend on quality images of their items in order to appeal to potential buyers. Backgrounds distract away from the subject of any photo. As the vast majority of individuals do not have access to professional-grade photo equipment or editing software, backgrounds are difficult to remove.
In an attempt to overcome the aforementioned problem and achieve its business objectives, eBay engineered a feature that it calls Image-Clean Up. eBay claims that the feature makes the product more appealing and improves buyer trust.
Below is a video that demonstrates the feature:
Source: eBay for Business AU
To accomplish this, eBay claims that it uses a computer vision algorithm to process the photo using the user’s mobile phone processor.
To access the software, the user uploads photos, follow on-screen prompts, or chooses the “Edit Photo” option. An image cleanup icon is then presented. The output of the software algorithms determines both the user options and additional functionality of the software. More on this soon.
As for how the model determines foreground (item) and background, eBay claims that it used conditional random fields (CRF) in its models to assess how unknown pixels are “masked” in the photo. The output of the CRF algorithm determines the probability of a pixel being part of the foreground. The pixel is then “blended” into either the foreground or converted into a white background.
In addition, the company claims that it uses a second algorithmic factor called “separability” in determining “how difficult it is to separate foreground from background.” The company states that it uses the output of this algorithm to determine whether the software produces an “auto-cleanup” option for the user or not. Images that score close to 100% will remove the background without seller input.
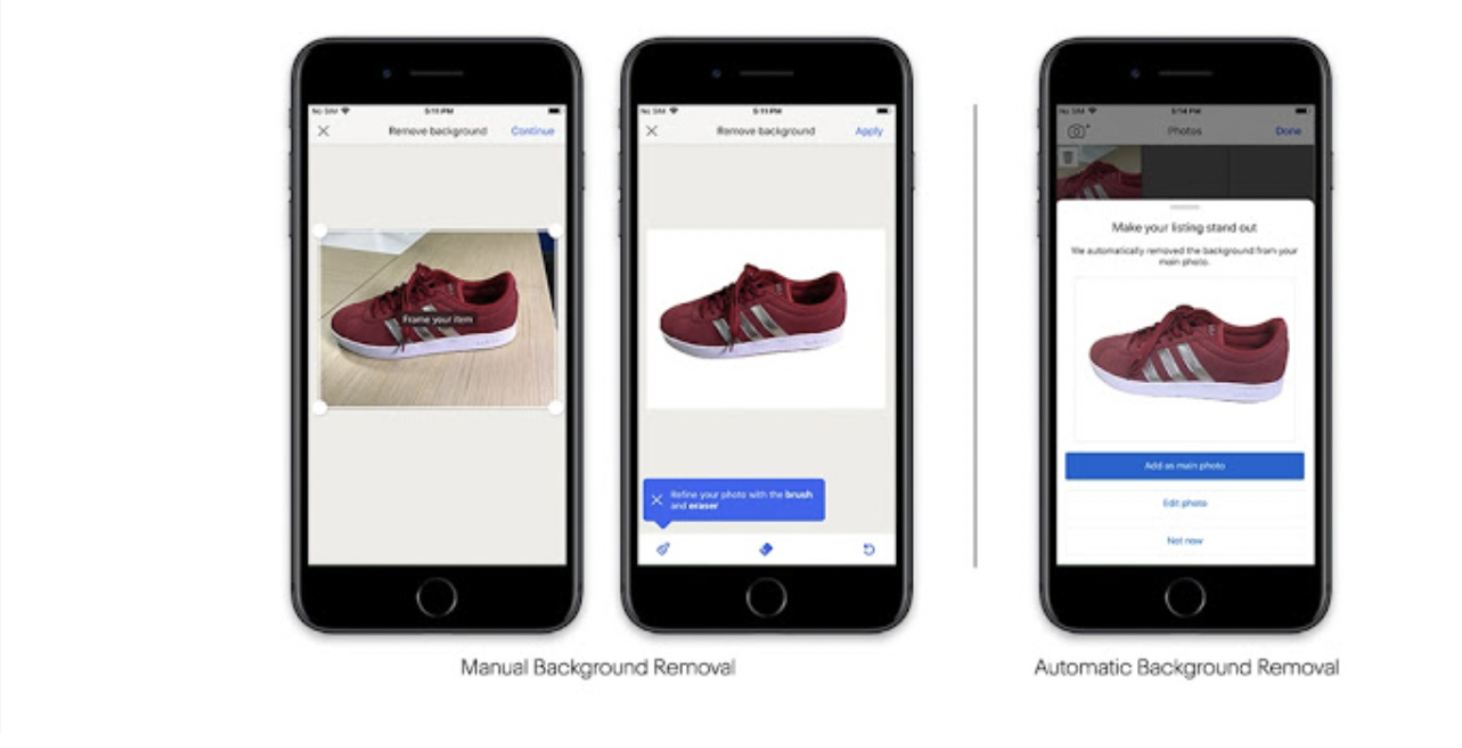
Regarding tangible business results of eBay’s imaging solution, the company claims that the image removal software has been a success. The company states that 76% of sellers that have used the feature used the result produced by the software without any manual modifications.


















