The food service industry is an economic staple generating billions of dollars in annual revenue and representing 2.1 percent of the U.S. GDP in 2016. Technology has made on-demand food ordering possible and the industry is pivoting towards more innovative approaches to meet and exceed customer expectations. As a result, artificial intelligence applications are steadily making their way into the food service industry.
In this article we explore applications of artificial intelligence in the food service industry to provide business leaders with an understanding of current and emerging trends, and popular use-cases that may change the way business is done.
Current applications of AI in the food service sector appear to fall into four major categories:
- Chatbots and Apps – Restaurants are using virtual assistants to respond to customer inquiries and to process and customize customer orders.
- Robots – Restaurants are using AI-driven robots to increase capacity and speed of food preparation and delivery.
- Recommendation engines – Developers are designing applications which use AI to help consumers choose meals based on their eating preferences.
- Kiosks – Restaurants are integrating AI-driven Kiosks to reduce customer waiting time and enhance the customer ordering experience.
We will begin by exploring chatbots and continue following the order of the applications listed above, providing representative examples for each category.
Restaurant Chatbots / Conversational Interfaces
Say2eat
New York-based startup Say2eat debuted in 2015 with a goal of helping chains and retailers improve customer engagement through chatbots. The company claims that by texting their favorite restaurants customers can order food through a branded and customized chatbot. Say2eats still functions through Facebook Messenger, Amazon Echo and SMS.
CEO and Founder Li-Ran Navon provides an explanation of how Say2eat works in the video below:
The move towards integrating more mobile solutions to enhance the customer engagement experience is consistent with industry research. A research report by Hospital Technology suggests that improving customer engagement through digital platforms is the leading strategic goal for tech investments in 2017 as indicated in the graph below:
Dominoes
In February 2017, Domino’s Pizza claims to have enhanced its Facebook Messenger chatbot, coordinating the release of its new features with the Super Bowl. The AI application named “Dom” allows consumers to begin placing an order by sending a message that only contains the word “Pizza”. Updates that were implemented into the system allow customers to order additional menu items such as wings and salads. Dominoes app
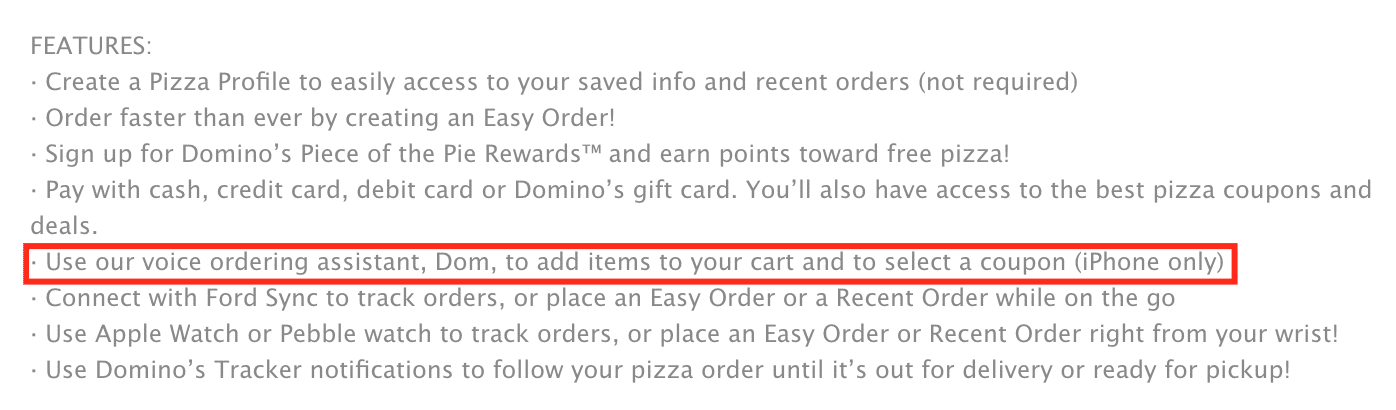
It should be noted that in the press release, the company does not provide data specific to the chatbot’s performance or how Domino’s expects the reported enhancements to improve customer engagement beyond the Super Bowl.
Domino’s attributes its estimated $4.7 billion in “global digital sales” in 2015 to its investments in innovative technology. However, the company does not provide any specifics regarding Other technologies include mobile apps, a GPS Driver tracker for delivery orders and a “pizza tracker” for smart watches. The company’s emphasis on the integration of technology into their customer service reflects an industry-wide food service trend.
Food Service and Restaurant Robots
Miso Robotics
California-based Miso Robotics is a startup focused on AI-driven robotic solutions for the kitchen environment. The company’s flagship AI kitchen assistant, “Flippy,” assists with grilling, frying, prepping and plating. The robot functions using software integrated with sensors and cameras allowing it to “see” the food it is helping to prepare and monitor important features such as temperature control.
The fast-food sector is a challenging area for employee retention. Within the larger sector of restaurants-and-accommodations, the estimated employee turnover rate was 72.9 percent in 2016. Another contributing factor to this trend is the increasing minimum wage. In 2017, minimum wage increases were documented in 19 states and other states are expected make increases in the coming years.
Cali Group the team behind fast-food chain CaliBurger announced a partnership in March 2017 with Miso Robotics to bring Flippy’s bugger flipping capabilities to its restaurants. Flippy was first installed in a Pasadena, California location and by 2019, CaliBurger will reportedly expand Flippy to over 50 locations worldwide.
Miso Robotics provides a demonstration of Flippy in action in the video below:
Pepper
Japanese technology firm SoftBank has collaborated with MasterCard to generate an AI-driven humanoid robot called Pepper. Pepper is a robot waiter that processes customer orders, provides product recommendations and allows customers to make payments via their Mastercard account by using the robot’s handheld tablet.
Watch pepper interact with a customer and help them place their order in the demonstration video below:
The company claims that users are able to speak to the robot with a normal speech pattern that would be used with a human waiter. Nestle’ engaged Pepper robots back in 2014 to enhance selling of the company’s coffee makers in Japan. Nestle’ reported that the robot would expand from 20 to 1,000 store locations by the end of 2015.
Pizza Hut has purchased several Pepper robots for use in its Asian restaurants. Designed to emphasize ease of use and payment security, the customer-operated touch screen tablet is powered by MasterPass, MasterCard’s global digital payment service. We covered some of Pepper’s other initial use-cases in our recent retail robotics article.
Food Service Apps
Halla
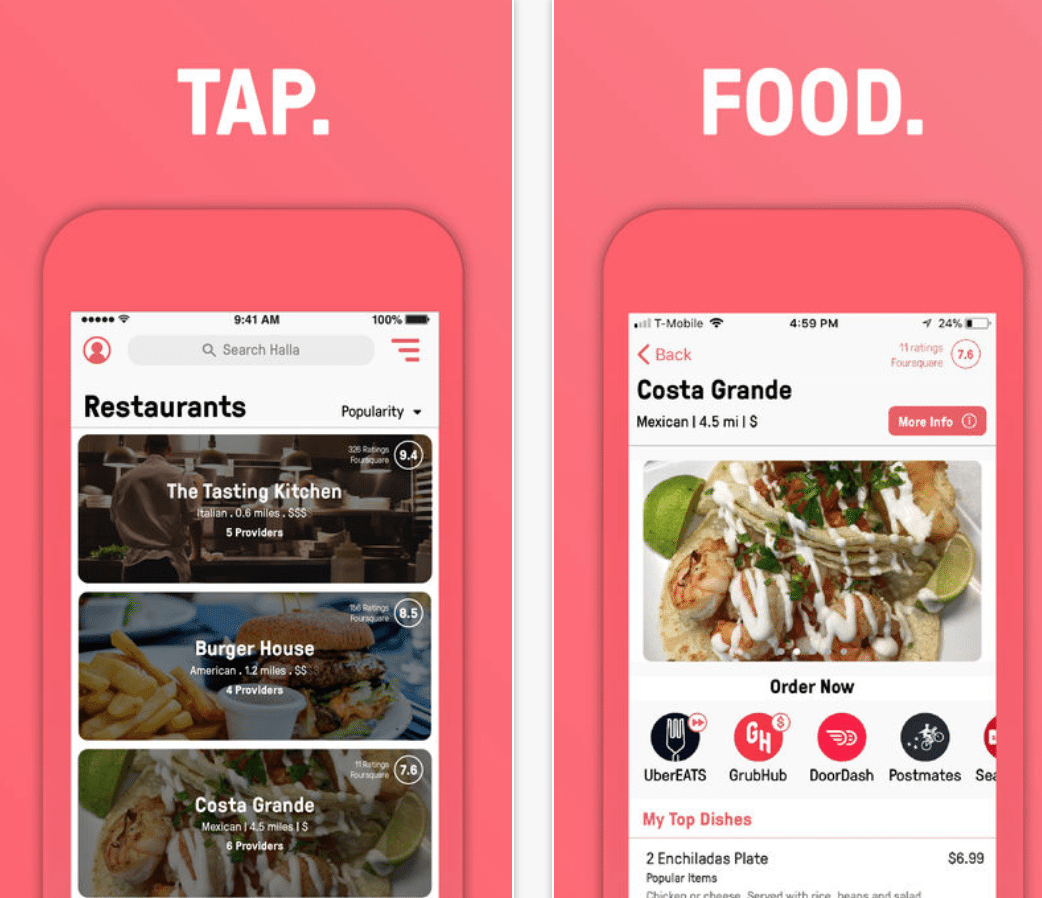
Founded in 2016 the Los Angeles based company Halla is a personalized restaurant and dining search engine. Currently available exclusively on iPhone and Apple technology, the company claims to make food delivery more convenient by providing access to several food delivery applications through one system.
Through the use of the recommendation engine, customers are matched with entrees and dining experiences that correspond with their pre-selected taste profile and specifications. Halla identifies and utilizes the patterns of a customer’s dining choices and location to link them to other restaurants that are likely to be of interest.
As of April 2017, the company has reportedly responded to over 17,000 queries, making 200,000 restaurant and meal recommendations. Halla claims that it has built its database by indexing and analyzing attributes found within 21 million dishes served at roughly 400,000 restaurants across the country.
To offer a glimpse of the company’s potential business interests, in the press release, a comparison is drawn between the goal’s of Halla and Pandora’s technology. Other noted recommendation engine companies mentioned include Netflix and Amazon.
“For the first time ever, people are spending more money at restaurants and bars than they’re spending on grocery shopping — a fact that demonstrates a huge shift in the way people are consuming and ultimately, enjoying food” says Halla CMO Spencer Price.
Halla claims to break down dishes the way Pandora or Spotify break down songs – analyzing common patterns (in this case – of flavor or ingredients, not of sound or rhythm) to suggest restaurants that have meals to suit what the user wants most.
(Readers with a more serious interest in recommendation engines should refer our complete article on recommendation system use cases.)
TellSpec USA
TellSpec, an AI company founded in 2013, utilizes AI in its handheld Food Sensor scanner to identify the contents of food at a molecular level.
Through the use of algorithms, the TellSpec scanner beams a light directly onto the food item. Light photons read chemical compounds which are then uploaded and processed through TellSpec’s analytics system. As a final result, data concerning the food’s composition will be processed through via Bluetooth and subsequently downloaded to the user’s smartphone.
Through its food item analysis process, TellSpec claims to identify possibly harmful substances in food products. In addition to potential harmful substances for the consumer such as allergens TellSpec identifies calories, macronutrients and certain nutritional information.
TellSpec provides a helpful demo of how its food scanner technology functions as shown in the video below:
From the company’s website it appears that TellSpec seeks partnerships with restaurants who are interested in disclosing the nutritional value of menu items to their customers.The product is also geared towards individuals with food sensitivities and special dietary needs.
In addition to AI, TellSpec technology reportedly incorporates bioinformatics, near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy, and predictive analytics.
While the company’s website does not offer data on the current number of users, the company does appears to segment its target clients into four categories:
- Distributors of the TellSpec food scanner
- Restaurants/Chefs
- Collaborations with developers and researchers
- Supermarkets and agriculture suppliers
Food safety is a major public health challenge and the USDA has reportedly invested over $70 million into food safety research, education and extension projects in an effort to build out a “farm-to-fork system” that is more effective and sustainable. This provides an indication of the relevance of innovative food inspection technologies
KFC
Working in collaboration with Chinese search engine giant Baidu, KFC is developing a restaurant that uses AI face recognition technology to infer what a customer may be interested in ordering – based on their sex, facial expressions, and other visual features.
The following video provides a quick example of how KFC is using this technology:
KFC has selected one of its Chinese restaurant locations to debut implementation of the Kiosk technology. Customers faces are scanned in an effort to identify personal characteristics that may influence food choices such as age, gender and current mood. The system is designed to process these customer’s characteristics and offer a menu item before the customer makes a selection.
The technology that the system utilizes will retain its scan of each customer’s face so that returning customers will be provided with recommendations based on their previous order history. Data security will be an important consideration for the companies as they advance this collaboration.
KFC’s face-scanning technology appears to still be in the early phase; a specific restaurant opening date was not provided in the press release. If the technology proves successful, it could have substantial impacts on the Chinese fast-food consumer market particularly among younger populations. Youth appear to be a target market as “the new restaurant will also offer augmented reality games as do 300 other KFC locations in the city.”
Other emerging Kiosk initiatives from competing restaurant chains include McDonald’s and Wendy’s with installation/purchasing costs estimated at $50,000 and $15,000, respectively per kiosk. However, it is important to clarify that these use cases are more traditional self-service Kiosks initiatives in comparison to KFC’s emerging initiative.
Concluding Thoughts
Across the food service sector, efforts are underway to capture and retain customer interest and business through AI-driven technologies. Chatbots tend to be one of the simpler applications for brands to launch across industries, so it’s no surprise that restaurants are employing these bots to engage customers.
Facebook Messenger remains a popular platform for chatbots and an estimated 90 percent of businesses are using Facebook to respond to customer inquiries. At this rate, the platform should continue to sustain its value for restaurants in the near future. However, due to the competitiveness and rate of change of social media platforms, predominantly Twitter and Facebook in the business space, it may be limiting for businesses to rely predominantly on the chatbot model in the long term.
Robots are an attractive emerging technology in the food service sector with the ability to entice customers. However, this is a technology which will require more fine tuning and improvement before widespread implementation can be expected. Robot dexterity in handling food and navigating between customers is a difficult challenge, and present applications in Asia have struggled.
For example, recent malfunctions of robot waiters in China, prompted restaurant owners to discontinue their use. Another barrier to implementation is cost. Robots of this kind are estimated at $7,700 per unit and require hundreds of dollars per month for general maintenance. Robot developers will need to guarantee that this technology is worth the investment over the long haul.
With a deluge of apps on the market, AI-driven food service apps like Halla will need to standout against the competition. Customizing the user experience for finding restaurants and meals of preference makes good business sense but demonstrating how this technology truly differs from more familiar platforms like Yelp may require additional time.
Self-service kiosks are a promising technology for restaurants seeking to reduce customer waiting times and increase order processing capacity. The global kiosk market is projected to reach an estimated $83.5 billion by 2021. With sizeable investments made by industry leaders such as McDonald’s and Wendy’s, in the next three to five years we anticipate more widespread adoption of this technology.
However, the example of KFC’s emerging facial recognition kiosk could, if successful, quickly become a major disruptor of traditional self-service kiosks in the fast-food sector.
Emerj has explored more emerging AI applications in the fast food sector, for readers interested in delving deeper into this topic.
Header image credit: Acorn Food Services




















