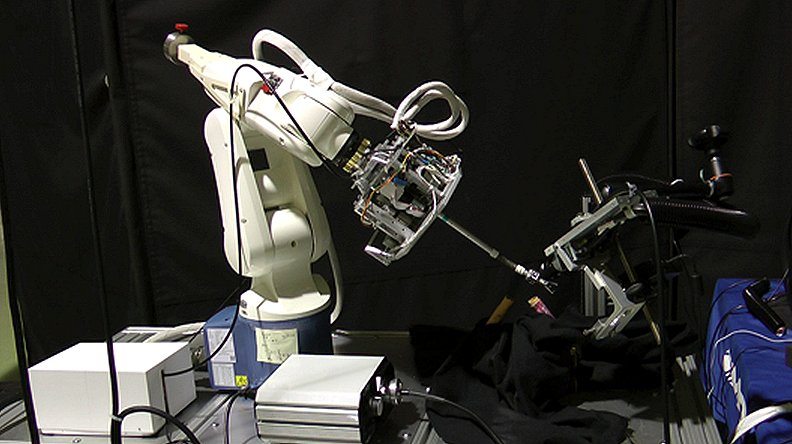
Pediatric Robot Surgeon
According to a recent report from NASA, some of their engineers and a team of researchers from The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) have recently developed a robotic surgical arm. Known as KidsArm, the robot has an external positioning system and is roughly the same size as a human arm. The robot will allow surgeons to easily explore surgical sites within a patient’s body and automate specific tasks to make pediatric surgery less invasive. The arm is still undergoing testing so that its dexterity can be fine-tuned. Potentially, KidsArm could greatly reduce the cost of surgical procedures, as well as improve the precision and consistency of patient interventions.
Nanoparticles for Tissue Regeneration
When you suffer an injury that damages your body’s tissues, this triggers an inflammatory response which stimulates repair and regeneration. However, this same response can be detrimental in situations where foreign materials, such as skin grafts, are being introduced. Researcher Arun Sharma and his team have developed a technology that can boost tissue regeneration. According to a report at phys.org, this innovative approach uses peptide-based molecules that have the ability to self-assemble into nanofibers. The resulting nanomaterials are biodegradable and biocompatible. They can potentially be used in a wide range of medical applications in the treatment of inflammatory-based conditions such as urinary tract infection.
‘Robo Brain’ to use World Wide Web to Instruct Robots
It’s inevitable that robots will become increasingly popular in our workplaces, homes and many other facilities. For this reason, researchers at Cornell have developed Robo Brain to capture information from the World Wide Web that it will use to instruct other robots. TechCrunch reports that the system scours the Internet and stores the information in the cloud. It can later transmit images and videos to other machines so they can learn how to think. Although the system has been in use for several years, it is now proving to be effective, particularly at helping robots manipulate objects. For example, if a robot sees a coffee mug, it can learn from Robo Brain what the object is, its uses and how it can be manipulated.
Image Credit: NASA